rabacus.rad_src package¶
Submodules¶
rabacus.rad_src.background module¶
An isotropic background radiation source module.
-
class
rabacus.rad_src.background.BackgroundSource(q_min, q_max, spectrum_type, Nnu=128, segmented=True, px_fit_type='verner', verbose=False, z=None, T_eff=None, alpha=None, user_E=None, user_shape=None)[source]¶ Bases:
rabacus.rad_src.source.SourceAn isotropic background radiation source class.
Args:
q_min (float): minimum photon energy / Rydbergs [dimensionless]
q_max (float): maximum photon energy / Rydbergs [dimensionless]
spectrum_type (str): the spectral shape {
monochromatic,hm12,thermal,powerlaw,user}Kwargs:
Nnu (int): number of spectral samples, log spaced in energy
segmented (bool): if
True, forces spectral samples at H and He ionization thresholdspx_fit_type (str): source to use for photoionization cross section fits {
verner}verbose (bool): verbose screen output?
z (float): redshift, need if spectrum_type =
hm12T_eff (float): effective temperature, need if spectrum_type =
thermalalpha (float): powerlaw index, need if spectrum_type =
powerlawuser_E (array): energy samples for user defined spectrum. should have units of energy.
user_shape (array): shape of user defined spectrum. should be dimensionless
Attributes:
U (
Units)PC (
PhysicalConstants)H (
Hydrogen)He (
Helium)PX (
PhotoXsections)E (array): Spectrum energy samples
lam (array): Spectrum wavelength samples
nu (array): Spectrum frequency samples
q (array): Spectrum energy samples / Rydbergs
Inu (array): Specific intensity
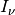
monochromatic (bool):
Truefor monochromatic spectra otherwiseFalsegrey (object): Grey photoionization cross sections and energies. Only created if segmented =
True.log (object): Convenience object storing the log of other attributes
sigma (object): photoionization cross sections and ratios
th (object): all quantities evaluated at ionization thresholds
thin (object): all optically thin quantities
Notes:
The fundamental characterization of the radiation field for this class is the specific intensity
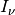 with units of
with units of erg/(s cm^2 sr Hz)or units oferg/(s cm^2 sr)for monochromatic spectra. Integrating over frequency and solid angle yields several other useful characterizations of the radiation field which we summarize below.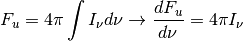
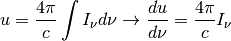
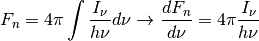
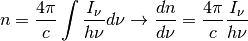
Variable Description Units Symbol Inu specific intensity [erg/(s cm^2 sr Hz)] 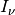
thin.Fu energy flux [erg/(s cm^2)] 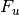
thin.u energy density [erg/(cm^3)] 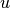
thin.Fn photon flux [1/(s cm^2)] 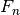
thin.n photon density [1/(cm^3)] 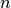
The photoionization and photoheating rates are also integrals over the specific intensity.
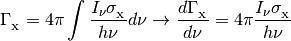
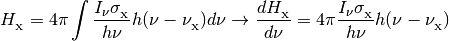
where
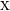 is one of
is one of
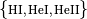 .
Note that the
.
Note that the 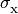 are frequency dependent
photoionization cross sections and the
are frequency dependent
photoionization cross sections and the 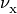 are
(scalar) frequencies that correspond to the ionization energies for a
given species. In many applications, we prefer to use energy as a
variable instead of frequency. The above equations can easily be recast
with a change of variable
are
(scalar) frequencies that correspond to the ionization energies for a
given species. In many applications, we prefer to use energy as a
variable instead of frequency. The above equations can easily be recast
with a change of variable 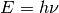 .
.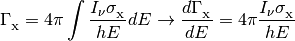
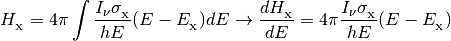
where the
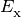 are (scalar) ionization energies.
are (scalar) ionization energies.Variable Description Units Symbol thin.H1i H1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 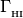
thin.He1i He1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 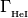
thin.He2i He2 photo ion. rate [1/s] 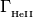
thin.H1h H1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 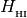
thin.He1h He1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 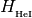
thin.He2h He2 photo heat rate [erg/s] 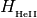
In addition, the class provides methods for calculating the shielded photoionization/heating rates given an optical depth.
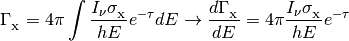
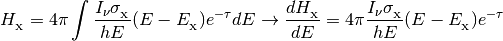
where
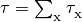 ,
,
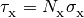 ,
,
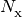 are column densities, and
are column densities, and
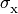 are energy dependent photoionization cross
sections.
are energy dependent photoionization cross
sections.Note
The
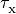 are energy dependent optical depths while the
parameters to the shielding functions (
are energy dependent optical depths while the
parameters to the shielding functions (shld_H1i(),shld_H1h(),shld_He1i(),shld_He1h(),shld_He2i(),shld_He2h()) are the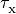 evaluated at the
species threhold energy (i.e. scalars).
evaluated at the
species threhold energy (i.e. scalars).Function Description Units Symbol shld_H1i H1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 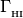
shld_He1i He1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 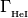
shld_He2i He2 photo ion. rate [1/s] 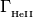
shld_H1h H1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 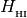
shld_He1h He1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 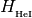
shld_He2h He2 photo heat rate [erg/s] 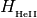
See also
-
normalize_H1i(H1i)[source]¶ Normalize the spectrum such that the H1 photoionization rate integral yields H1i.
- Args:
- H1i (float): target photoionization rate
-
normalize_n(n)[source]¶ Normalize the spectrum such that the number density of photons between q_min and q_max is n.
- Args:
- n (float): target photon number density
-
return_attenuation(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Calculate the attenuation array. First the energy dependence of tau for each absorbing species (H1, He1, He2) is calculated using the input scalar optical depths at the ionization thresholds. Next an energy dependent total tau is calculated and exponentiated to arrive at the attenuation array atten = np.exp(-tau).
Args:
tauH1_th (float): H1 optical depth at the H1 ionizing threshold
tauHe1_th (float): He1 optical depth at the He1 ionizing threshold
tauHe2_th (float): He2 optical depth at the He2 ionizing threshold
Returns:
atten (array): attenuation as a function of energy
-
scale_spectrum(fac)[source]¶ Changes normalization of spectrum and recalculates spectral integrands.
- Args:
- fac (float): multiplicative factor
-
set_integrands()[source]¶ Defines tabulated functions of photon energy/frequency which represent integrands for optically thin quantities. All attributes defined in this function are integrands of the fundamental quantity, specific intensity or Inu which has units [erg/(s Hz cm^2 sr)].
-
shld_H1h(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HI photoheating rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau
- Args:
tauH1_th (float): H1 optical depth at the H1 ionizing threshold
tauHe1_th (float): He1 optical depth at the He1 ionizing threshold
tauHe2_th (float): He2 optical depth at the He2 ionizing threshold
- Returns:
- H1h (float): attenuated H1 photoheating rate
-
shld_H1i(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HI photoionization rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau
- Args:
tauH1_th (float): H1 optical depth at the H1 ionizing threshold
tauHe1_th (float): He1 optical depth at the He1 ionizing threshold
tauHe2_th (float): He2 optical depth at the He2 ionizing threshold
- Returns:
- H1i (float): attenuated H1 photoionization rate
-
shld_He1h(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HeI photoheating rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau.
See also
-
shld_He1i(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HeI photoionization rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau.
See also
-
shld_He2h(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HeII photoheating rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau.
See also
-
rabacus.rad_src.hm12 module¶
A module for loading the Haardt and Madau 2012 spectral model
(see HM12_UVB_Table).
The returned spectrum will be normalized as in the HM12 model. Further
adjustments to normalization are handled through classes derived from
Source.
rabacus.rad_src.monochromatic module¶
A module for loading monochromatic spectra. This module is only here to
conform to the style of the other spectral shapes. Normalization is handled
through classes derived from Source.
rabacus.rad_src.plane module¶
An plane parallel radiation source class.
-
class
rabacus.rad_src.plane.PlaneSource(q_min, q_max, spectrum_type, Nnu=128, segmented=True, px_fit_type='verner', verbose=False, z=None, T_eff=None, alpha=None, user_E=None, user_shape=None)[source]¶ Bases:
rabacus.rad_src.source.SourceA plane parallel radiation source class.
Args:
q_min (float): minimum photon energy / Rydbergs [dimensionless]
q_max (float): maximum photon energy / Rydbergs [dimensionless]
spectrum_type (str): the spectral shape {
monochromatic,hm12,thermal,powerlaw,user}Kwargs:
Nnu (int): number of spectral samples, log spaced in energy
segmented (bool): if
True, forces spectral samples at H and He ionization thresholdspx_fit_type (str): source to use for photoionization cross section fits {
verner}verbose (bool): verbose screen output?
z (float): redshift, need if spectrum_type =
hm12T_eff (float): effective temperature, need if spectrum_type =
thermalalpha (float): powerlaw index, need if spectrum_type =
powerlawuser_E (array): energy samples for user defined spectrum. should have units of energy.
user_shape (array): shape of user defined spectrum. should be dimensionless
Attributes:
U (
Units)PC (
PhysicalConstants)H (
Hydrogen)He (
Helium)PX (
PhotoXsections)E (array): Spectrum energy samples
lam (array): Spectrum wavelength samples
nu (array): Spectrum frequency samples
q (array): Spectrum energy samples / Rydbergs
dFu_over_dnu (array): Energy flux density
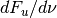
monochromatic (bool):
Truefor monochromatic spectra otherwiseFalsegrey (object): Grey photoionization cross sections and energies. Only created if segmented =
True.log (object): Convenience object storing the log of other attributes
sigma (object): photoionization cross sections and ratios
th (object): all quantities evaluated at ionization thresholds
thin (object): all optically thin quantities
Notes:
The fundamental characterization of the radiation field for this class is the energy flux density
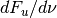 with units of
with units of erg/(s cm^2 Hz)or energy flux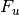 with units of
with units of erg/(s cm^2)for monochromatic spectra. Integrating over frequency yields several other useful characterizations of the radiation field which we summarize below.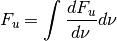
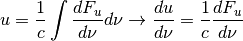
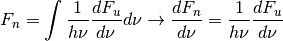
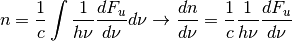
Variable Description Units Symbol dFu_dnu energy flux density [erg/(s cm^2 Hz)] 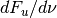
thin.Fu energy flux [erg/(s cm^2)] 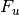
thin.u energy density [erg/(cm^3)] 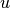
thin.Fn photon flux [1/(s cm^2)] 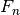
thin.n photon density [1/(cm^3)] 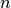
The photoionization and photoheating rates are also integrals over the energy flux density.
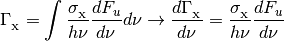
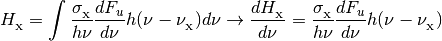
where
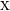 is one of
is one of
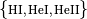 .
Note that the
.
Note that the 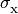 are frequency dependent
photoionization cross-sections and the
are frequency dependent
photoionization cross-sections and the 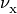 are
(scalar) frequencies that correspond to the ionization energies for a given
species. In many applications, we prefer to use energy as a variable
instead of frequency. The above equations can easily be recast with a
change of variable
are
(scalar) frequencies that correspond to the ionization energies for a given
species. In many applications, we prefer to use energy as a variable
instead of frequency. The above equations can easily be recast with a
change of variable 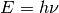 .
.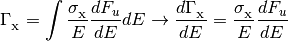
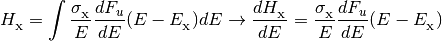
where the
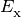 are (scalar) ionization energies.
are (scalar) ionization energies.Variable Description Units Symbol thin.H1i H1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 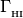
thin.He1i He1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 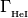
thin.He2i He2 photo ion. rate [1/s] 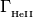
thin.H1h H1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 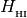
thin.He1h He1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 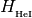
thin.He2h He2 photo heat rate [erg/s] 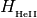
In addition, the class provides methods for calculating the shielded photoionization/heating rates given an optical depth.
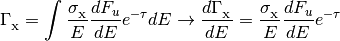
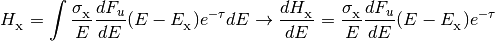
where
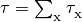 ,
,
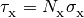 ,
,
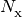 are column densities, and
are column densities, and
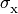 are energy dependent photoionization cross
sections.
are energy dependent photoionization cross
sections.Note
The
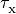 are energy dependent optical depths while the
parameters to the shielding functions (
are energy dependent optical depths while the
parameters to the shielding functions (shld_H1i(),shld_H1h(),shld_He1i(),shld_He1h(),shld_He2i(),shld_He2h()) are the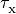 evaluated at the
species threhold energy (i.e. scalars).
evaluated at the
species threhold energy (i.e. scalars).Function Description Units Symbol shld_H1i H1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 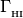
shld_He1i He1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 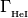
shld_He2i He2 photo ion. rate [1/s] 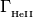
shld_H1h H1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 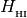
shld_He1h He1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 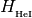
shld_He2h He2 photo heat rate [erg/s] 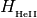
See also
-
normalize_Fn(Fn)[source]¶ Normalize the spectrum such that the photon flux between q_min and q_max is Fn.
- Args:
- Fn (float): target photon flux
-
normalize_H1i(H1i)[source]¶ Normalize the spectrum such that the H1 photoionization rate integral yields H1i.
- Args:
- H1i (float): target photoionization rate
-
normalize_n(n)[source]¶ Normalize the spectrum such that the number density of photons between q_min and q_max is n.
- Args:
- n (float): target photon number density
-
return_attenuation(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Calculate the attenuation array. First the energy dependence of tau for each absorbing species (H1, He1, He2) is calculated using the input scalar optical depths at the ionization thresholds. Next an energy dependent total tau is calculated and exponentiated to arrive at the attenuation array atten = np.exp(-tau).
Args:
tauH1_th (float): H1 optical depth at the H1 ionizing threshold
tauHe1_th (float): He1 optical depth at the He1 ionizing threshold
tauHe2_th (float): He2 optical depth at the He2 ionizing threshold
Returns:
atten (array): attenuation as a function of energy
-
scale_spectrum(fac)[source]¶ Changes normalization of spectrum and recalculates spectral integrands.
- Args:
- fac (float): multiplicative factor
-
set_integrands()[source]¶ Defines tabulated functions of photon energy/frequency which represent integrands for optically thin quantities. All attributes defined in this function are integrands of the fundamental quantity, energy flux density or dFu_over_dnu which has units [erg/(s cm^2 Hz)].
-
shld_H1h(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HI photoheating rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau
- Args:
tauH1_th (float): H1 optical depth at the H1 ionizing threshold
tauHe1_th (float): He1 optical depth at the He1 ionizing threshold
tauHe2_th (float): He2 optical depth at the He2 ionizing threshold
- Returns:
- H1h (float): attenuated H1 photoheating rate
-
shld_H1i(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HI photoionization rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau
- Args:
tauH1_th (float): H1 optical depth at the H1 ionizing threshold
tauHe1_th (float): He1 optical depth at the He1 ionizing threshold
tauHe2_th (float): He2 optical depth at the He2 ionizing threshold
- Returns:
- H1i (float): attenuated H1 photoionization rate
-
shld_He1h(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HeI photoheating rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau.
See also
-
shld_He1i(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HeI photoionization rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau.
See also
-
shld_He2h(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HeII photoheating rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau.
See also
-
rabacus.rad_src.point module¶
A point radiation source class.
-
class
rabacus.rad_src.point.PointSource(q_min, q_max, spectrum_type, Nnu=128, segmented=True, px_fit_type='verner', verbose=False, z=None, T_eff=None, alpha=None, user_E=None, user_shape=None)[source]¶ Bases:
rabacus.rad_src.source.SourceA point radiation source class.
Args:
q_min (float): minimum photon energy / Rydbergs [dimensionless]
q_max (float): maximum photon energy / Rydbergs [dimensionless]
spectrum_type (str): the spectral shape {
monochromatic,hm12,thermal,powerlaw,user}Kwargs:
Nnu (int): number of spectral samples, log spaced in energy
segmented (bool): if
True, forces spectral samples at H and He ionization thresholdspx_fit_type (str): source to use for photoionization cross section fits {
verner}verbose (bool): verbose screen output?
z (float): redshift, need if spectrum_type =
hm12T_eff (float): effective temperature, need if spectrum_type =
thermalalpha (float): powerlaw index, need if spectrum_type =
powerlawuser_E (array): energy samples for user defined spectrum. should have units of energy.
user_shape (array): shape of user defined spectrum. should be dimensionless
Attributes:
U (
Units)PC (
PhysicalConstants)H (
Hydrogen)He (
Helium)PX (
PhotoXsections)E (array): Spectrum energy samples
lam (array): Spectrum wavelength samples
nu (array): Spectrum frequency samples
q (array): Spectrum energy samples / Rydbergs
dLu_over_dnu (array): Energy luminosity density
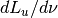
monochromatic (bool):
Truefor monochromatic spectra otherwiseFalsegrey (object): Grey photoionization cross sections and energies. Only created if segmented =
True.log (object): Convenience object storing the log of other attributes
sigma (object): photoionization cross sections and ratios
th (object): all quantities evaluated at ionization thresholds
thin (object): all optically thin quantities
Notes:
The fundamental characterization of the radiation field for this class is the energy luminosity density
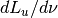 with units of
with units of erg/(s Hz)or energy luminosity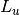 with units of
with units of erg/sfor monochromatic spectra. All quantities except for the luminosity are dependent on radius. We summarize them below,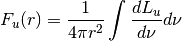
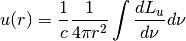
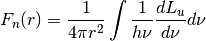
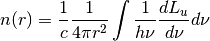
Variable Description Units Symbol dLu_dnu energy lum. density [erg/(s Hz)] 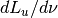
thin.Fu energy flux [erg/(s cm^2)] 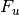
thin.u energy density [erg/(cm^3)] 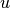
thin.Fn photon flux [1/(s cm^2)] 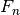
thin.n photon density [1/(cm^3)] 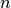
The photoionization and photoheating rates are also integrals over the energy luminosity density.
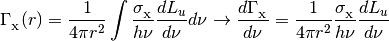
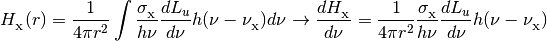
where
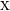 is one of
is one of
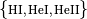 .
Note that the
.
Note that the 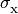 are frequency dependent
photoionization cross-sections and the
are frequency dependent
photoionization cross-sections and the 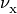 are
(scalar) frequencies that correspond to the ionization energies for a given
species. In many applications, we prefer to use energy as a variable
instead of frequency. The above equations can easily be recast with a
change of variable
are
(scalar) frequencies that correspond to the ionization energies for a given
species. In many applications, we prefer to use energy as a variable
instead of frequency. The above equations can easily be recast with a
change of variable 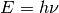 .
.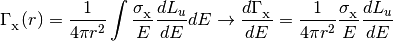
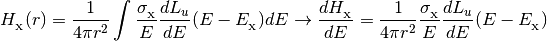
where the
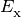 are (scalar) ionization energies.
are (scalar) ionization energies.Variable Description Units Symbol thin.H1i H1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 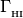
thin.He1i He1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 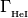
thin.He2i He2 photo ion. rate [1/s] 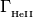
thin.H1h H1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 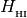
thin.He1h He1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 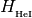
thin.He2h He2 photo heat rate [erg/s] 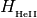
In addition, the class provides methods for calculating the shielded photoionization/heating rates given an optical depth.
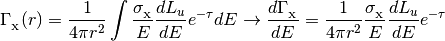
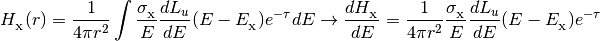
where
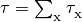 ,
,
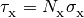 ,
,
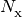 are column densities, and
are column densities, and
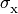 are energy dependent photoionization cross
sections.
are energy dependent photoionization cross
sections.Note
The
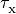 are energy dependent optical depths while the
parameters to the shielding functions (
are energy dependent optical depths while the
parameters to the shielding functions (shld_H1i(),shld_H1h(),shld_He1i(),shld_He1h(),shld_He2i(),shld_He2h()) are the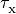 evaluated at the
species threhold energy (i.e. scalars).
evaluated at the
species threhold energy (i.e. scalars).Function Description Units Symbol shld_H1i H1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 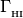
shld_He1i He1 photo ion. rate [1/s] 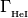
shld_He2i He2 photo ion. rate [1/s] 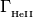
shld_H1h H1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 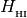
shld_He1h He1 photo heat rate [erg/s] 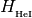
shld_He2h He2 photo heat rate [erg/s] 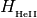
See also
-
normalize_Ln(Ln)[source]¶ Normalize spectrum such that the photon luminosity is Ln.
- Args:
- Ln (float): target photon luminosity
-
normalize_Lu(Lu)[source]¶ Normalize spectrum such that the energy luminosity is Lu.
- Args:
- Lu (float): target energy luminosity
-
return_attenuation(tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Calculate the attenuation array. First the energy dependence of tau for each absorbing species (H1, He1, He2) is calculated using the input scalar optical depths at the ionization thresholds. Next an energy dependent total tau is calculated and exponentiated to arrive at the attenuation array atten = np.exp(-tau).
Args:
tauH1_th (float): H1 optical depth at the H1 ionizing threshold
tauHe1_th (float): He1 optical depth at the He1 ionizing threshold
tauHe2_th (float): He2 optical depth at the He2 ionizing threshold
Returns:
atten (array): attenuation as a function of energy
-
scale_spectrum(fac)[source]¶ Changes normalization of spectrum and recalculates spectral integrands.
- Args:
- fac (float): multiplicative factor
-
set_integrands()[source]¶ Defines tabulated functions of photon energy/frequency which represent integrands for optically thin quantities. All attributes defined in this function are integrands of the fundamental quantity, energy luminosity density or dLu_over_dnu which has units [erg/(s Hz)].
-
shld_H1h(r, tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HI photoheating rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau
- Args:
r (float): radial distance from point source
tauH1_th (float): H1 optical depth at the H1 ionizing threshold
tauHe1_th (float): He1 optical depth at the He1 ionizing threshold
tauHe2_th (float): He2 optical depth at the He2 ionizing threshold
- Returns:
- H1h (float): attenuated H1 photoheating rate
-
shld_H1i(r, tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HI photoionization rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau
- Args:
r (float): radial distance from point source
tauH1_th (float): H1 optical depth at the H1 ionizing threshold
tauHe1_th (float): He1 optical depth at the He1 ionizing threshold
tauHe2_th (float): He2 optical depth at the He2 ionizing threshold
- Returns:
- H1i (float): attenuated H1 photoionization rate
-
shld_He1h(r, tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HeI photoheating rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau.
See also
-
shld_He1i(r, tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HeI photoionization rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau.
See also
-
shld_He2h(r, tauH1_th, tauHe1_th, tauHe2_th)[source]¶ Integrates spectrum to calculate the HeII photoheating rate after passing through a column with optical depth tau.
See also
-
rabacus.rad_src.powerlaw module¶
A module for loading powerlaw spectra. This module is only concerned with
the shape of the spectrum. Normalization is handled through classes derived
from Source.
rabacus.rad_src.source module¶
Module for source base class.
-
class
rabacus.rad_src.source.Source[source]¶ Base class for radiation sources. Derive specific radiation source classes from this class. Cannot be directly instantiated. Note that all derived source classes call
initialize()when they are instanciated.See also
-
initialize(q_min, q_max, spectrum_type, Nnu, segmented, px_fit_type, verbose, z, T_eff, alpha, user_E, user_shape)[source]¶ Perform general initialization.
Args:
q_min (float): minimum photon energy / Rydbergs [dimensionless]
q_max (float): maximum photon energy / Rydbergs [dimensionless]
spectrum_type (str): the spectral shape {
monochromatic,hm12,thermal,powerlaw,user}Nnu (int): number of spectral samples, log spaced in energy
segmented (bool): if
True, forces spectral samples at H and He ionization thresholdspx_fit_type (str): source to use for photoionization cross section fits {
verner}verbose (bool): verbose screen output?
z (float): redshift, need if spectrum_type =
hm12T_eff (float): effective temperature, need if spectrum_type =
thermalalpha (float): powerlaw index, need if spectrum_type =
powerlawuser_E (array): energy samples for user defined spectrum. should have units of energy.
user_shape (array): shape of user defined spectrum. should be dimensionless
-
set_photon_arrays(q_min, q_max, Nnu, segmented)[source]¶ Creates wavelength, frequency, and energy arrays for the spectrum.
Args:
q_min (float): minimum photon energy / Rydbergs [dimensionless]
q_max (float): maximum photon energy / Rydbergs [dimensionless]
Nnu (int): number of spectral samples, log spaced in energy
segmented (bool): if
True, forces spectral samples at H and He ionization thresholds
-
rabacus.rad_src.species module¶
A module supplying containers for groups of ions.
rabacus.rad_src.thermal module¶
A module for loading blackbody spectra. This module is only concerned with
the shape of the spectrum. Normalization is handled through classes derived
from Source.
Module contents¶
A package containing classes which represent sources of radiation. To create a source, one needs to choose a geometry class and a spectral shape. The choices for geometry are:
When creating a source, instantiate a geometric source class and indicate
the spectral shape by setting the argument spectrum_type equal to one of
{monochromatic, powerlaw, thermal, hm12}. Note that the
spectral shape does not determine the normalization of the spectrum, therefore
classes will be returned with an arbitrary normalization. The exception
is the Haardt & Madau 2012 model which is returned with the normalization
native to the model. Each geometric class contains methods to (re)normalize
the spectrum.
Segmented Spectra¶
By default, the spectra created for sources will be segmented. This means that
an exactly uniform spacing of the energy samples in log energy space will be
sacrificed to guarantee that samples exist at the ionization thresholds of
neutral hydrogen, neutral helium, and singly ionized helium
(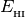 ,
, 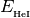 ,
, 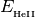 ).
If one tries to create a segmented spectrum in which the energy samples do not
cover the range between
).
If one tries to create a segmented spectrum in which the energy samples do not
cover the range between 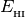 and
and 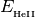 (see the q_min and q_max variables) an error will occur.
(see the q_min and q_max variables) an error will occur.
Grey Quantities¶
Frequency averaged or “grey” quantities will be calculated for any segmented
spectrum. We show an example for the
BackgroundSource
class here, but the principle is the same for all source types. The grey
photoionization cross sections are defined as follows,
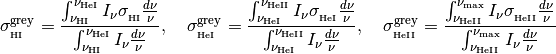
We can implicitly define a grey frequency and therefore a grey energy,
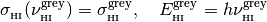
where similar relationships hold for the helium ions.
Examples¶
The following code will create a point source with a photon luminosity of 5.0e48 photons per second and a 1.0e5 K blackbody spectrum between 1 and 5 Rydbergs:
import rabacus as ra
q_min = 1.0; q_max = 5.0; T_eff = 1.0e5 * ra.U.K
pt_t1e5 = ra.rad_src.PointSource( q_min, q_max, 'thermal', T_eff=T_eff )
pt_t1e5.normalize_Ln( 5.0e48 / ra.U.s )
The following code will create a uniform background source with a spectral shape given by the model of Haardt and Madau 2012 at redshift 3 between 1 and 400 Rydbergs:
import rabacus as ra
q_min = 1.0; q_max = 4.0e2; z=3.0
bgnd_hm12 = ra.rad_src.BackgroundSource( q_min, q_max, 'hm12', z=z )
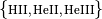 .
.