rabacus.cosmology package¶
Subpackages¶
Submodules¶
rabacus.cosmology.general module¶
A general FLRW cosmology module. Assumes a spatially flat universe.
-
class
rabacus.cosmology.general.Cosmology(cpdict, verbose=False, zlo=0.0, zhi=200.0, Nz=500)[source]¶ Bases:
objectGeneral Cosmology Class. Assumes a spatialy flat universe.
Args:
cpdict (dict) A dictionary of cosmological parameters. For example, seePlanckParameters.- The dictionray cpdict must include the following keys,
omegam-> current matter density in units of critical todayomegal-> current lambda density in units of critical todayomegab-> current baryon density in units of critical todayh-> Hubble parameter H0 = 100 h km/s/Mpcsigma8-> amplitude of fluctuations in spheres w/ R = 8 Mpc/hns-> slope of primordial power spectrumYp-> primordial mass fraction of helium
Attributes:
H0 (real): hubble parameter now,
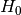 .
.OmegaB (real): baryon density / critical density now,
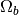
OmegaC (real): cold dark matter density / critical density now,
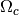
OmegaL (real): dark energy density / critical density now,
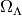
OmegaM (real): matter density / critical density now,
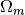
Yp (real): primoridial helium mass fraction,
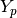
cu (
CosmoUnits): cosmological units which are aware of the hubble parameter.dH0 (real): hubble distance now,
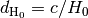
tH0 (real): hubble time now,
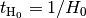
rho_crit0 (real): critical density now,
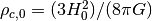
eps_crit0 (real): critical energy density now,
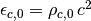
nH_crit0 (real): critical hydrogen number density now,
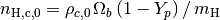
-
Dc_at_tL(tL)[source]¶ Comoving distance at a given lookback time, Dc(tL). First finds a redshift z by inverting the function
tLz()using tabulated values. Second, callsDcz()to get a comoving distance from z.![z = {\rm Inverse}[ t_L(z) ] \\
D_C(z) = d_{\rm H_0} \int_{0}^{z} \frac{dz'}{E(z')}](_images/math/58308a36a28d9ff7cac73f077d164e19fd35a669.png)
-
Dca(a)[source]¶ Comoving distance between a=1 and a, Dc(a). The scale factor a is converted to redshift z and then
Dcz()is called.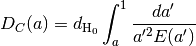
-
da2dDc(a1, a2)[source]¶ Comoving distance between a1 and a2. The scale factors a1 and a2 are converted to redshifts z1 and z2 and then
dz2dDc()is called. a1 < a2 produces positive comoving distance.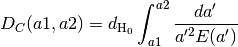
-
da2dtL(a1, a2)[source]¶ Lookback time between a1 and a2. Two calls to
tLa()are made and the results subtracted. a1 < a2 produces positive lookback time.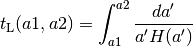
-
dz2dDc(z1, z2)[source]¶ Comoving distance between z1 and z2. Two calls to
Dcz()are made and the results subtracted. z1 < z2 produces positive comoving distance.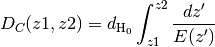
-
dz2dtL(z1, z2)[source]¶ Lookback time between z1 and z2. The redshifts z1 and z2 are converted to scale factors and then
da2dtL()is called. z1 < z2 produces positive lookback time.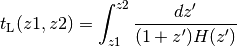
-
tL_at_Dc(Dc)[source]¶ Lookback time at a given comoving distance, tL(Dc). First finds a redshift z by inverting the function
Dcz()using tabulated values. Second, callstLz()to get a lookback time from z.![z = {\rm Inverse}[ D_C(z) ] \\
t_L(z) = \int_0^z \frac{dz'}{(1+z') H(z')}](_images/math/ebb4c007cac05418aaddcdfc2a3dee9137225de1.png)
rabacus.cosmology.jeans module¶
A general Jeans scale module.
-
class
rabacus.cosmology.jeans.Jeans(Yp=0.248, fg=0.154, gamma=1.6666666666666667)[source]¶ A Jeans scale class.
Provides access to Jeans scales functions. Default values for Yp and fg are taken from Planck Cosmological Parameters
Yp = 0.248 fg = Omega_b / Omega_m = 0.154
Args:
Kwargs:
Yp (float): helium mass fraction
fg (float): gas fraction
gamma (float): ratio of specific heats
-
L(nH, T, mu)[source]¶ Jeans length
Args:
nH (float): hydrogen number density
T (float): temperature
mu (float): mean molecular weight
-
NH(nH, T, mu)[source]¶ Jeans column density
Args:
nH (float): hydrogen number density
T (float): temperature
mu (float): mean molecular weight
-
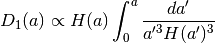
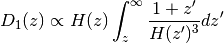
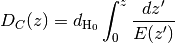
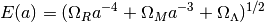
![E(z) = [ \Omega_R (1+z)^{4} + \Omega_M (1+z)^{3} +
\Omega_{\Lambda} ]^{1/2}](_images/math/d511792a660d34889a9b7056cdd37a27b8e284a7.png)
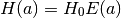
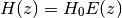
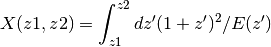
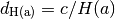
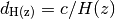
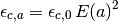
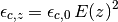
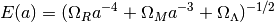
![E(z) = [ \Omega_R (1+z)^{4} + \Omega_M (1+z)^{3} +
\Omega_{\Lambda} ]^{-1/2}](_images/math/8d6f84b9ce1957cfcb434b6ebbc6145fa8419bd2.png)


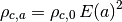
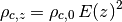
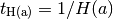
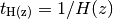
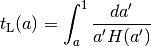
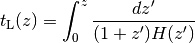
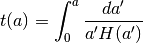
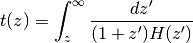
![z(D_C) = {\rm Inverse}[ D_C(z) ]](_images/math/ab7abc3dc39203f2926f3c0987f71f020df9a7de.png)
![z(t_L) = {\rm Inverse}[ t_L(z) ]](_images/math/2f6cbf4a8e969e419dc29850bfae02bb36c0a991.png)