caps.diffusion_estimation.tensor_scalars.SecondOrderScalarParameters¶
SecondOrderScalarParameters¶
- class caps.diffusion_estimation.tensor_scalars.SecondOrderScalarParameters[source]¶
Compute the Fractional Anisotropy [R3] (FA), Mean Diffusivity (MD) and the Westion Shapes coefficients [R3] (cl, cp, cs) of a second order tensor.
[+show/hide second order tensor scalars]
References
[R3] (1, 2) C. Westin, S. Maier, H. Mamata, A. Nabavi, F. Jolesz and R. Kikinis : Processing and visualization of diffusion tensor MRI. Medical Image Analysis, 6(2):93-108, 2002.
Inputs¶
[Mandatory]
eigenvalues_file: a file name (mandatory)
a second order tensor eigen values
|
[Optional]
cl_basename: a string (optional)
the basename of the output linearity coefficients file
|
cp_basename: a string (optional)
the basename of the output planarity coefficients file
|
cs_basename: a string (optional)
the basename of the output sphericity coefficients file
|
fa_basename: a string (optional)
the basename of the output fa file
|
md_basename: a string (optional)
the basename of the output md file
|
output_directory: a directory name (optional)
the output directory where the tensor scalars will be written
|
Outputs¶
fractional_anisotropy_file: a file name
the name of the output fa file
|
linearity_file: a file name
the name of the fie that contains the linerity coefficients
|
mean_diffusivity_file: a file name
the name of the output md file
|
planarity_file: a file name
the name of the fie that contains the planarity coefficients
|
sphericity_file: a file name
the name of the fie that contains the sphericity coefficients
|

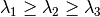 of the diffusion tensor as
follows:
of the diffusion tensor as
follows:
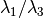 . When the
ellipse is elongated this measure increases. Unfortunately, this measure
is sensitive to measurement noise and do not take into account the second
eigenvalue. Another way to characterize the anisotropy is based on the
difference of the three eigenvalues,
. When the
ellipse is elongated this measure increases. Unfortunately, this measure
is sensitive to measurement noise and do not take into account the second
eigenvalue. Another way to characterize the anisotropy is based on the
difference of the three eigenvalues,
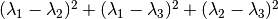 .
This measure is zero for a sphere (
.
This measure is zero for a sphere (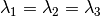 ) and
increases when the sphere is distorted. When this measure is normalized
between 0 and 1 the FA is obtained:
) and
increases when the sphere is distorted. When this measure is normalized
between 0 and 1 the FA is obtained: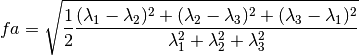
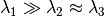 ): the
diffusion is mainly in the direction of the eigenvector associated with the
largest eigenvalue.
): the
diffusion is mainly in the direction of the eigenvector associated with the
largest eigenvalue.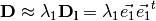
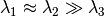 ): the
diffusion is in the plane defined by the two eigenvectors corresponding to the
two largest eigenvalues.
): the
diffusion is in the plane defined by the two eigenvectors corresponding to the
two largest eigenvalues.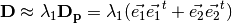
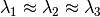 ): the
diffusion is isotropic.
): the
diffusion is isotropic.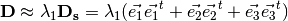
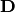 can be represented by combination of
these three cases:
can be represented by combination of
these three cases: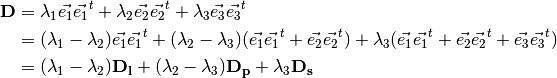
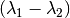 ,
, 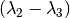 and
and
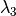 are the coordinates of
are the coordinates of ![[\mathbf{D_l}, \mathbf{D_p}, \mathbf{D_s}]](../../../_images/math/2f47cd3a1c51d6f62a48148e8c0ed00f54516640.png) . This
relationship between the eigenvalues of the diffusion tensor enables the
classification of the diffusion tensor from its geometric shape. Using this
new decomposition, it is possible to quantify the similarity to the linear,
planar and spherical cases. The coefficients obtained are normalized as follows:
. This
relationship between the eigenvalues of the diffusion tensor enables the
classification of the diffusion tensor from its geometric shape. Using this
new decomposition, it is possible to quantify the similarity to the linear,
planar and spherical cases. The coefficients obtained are normalized as follows: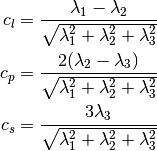
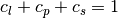 . These three factors provide additional
information characterizing the shape of a tensor. Finally, the anisotropy can
be measured as a difference with the spherical case:
. These three factors provide additional
information characterizing the shape of a tensor. Finally, the anisotropy can
be measured as a difference with the spherical case: