biostrings: handling genomic information as strings¶
The module reflects the content of the R/Bioconductor package Biostrings. It defines Python-level classes for the R/S4 classes, and gives otherwise access to R-level commands the usual rpy2:robjects way.
The variable biostrings_env in the module is an rpy2.robjects.REnvironment for the modules namespace. Accessing explicitly a module’s object is then straightforward. Example:
>>> biostrings.biostrings_env['RNA_ALPHABET']
The class inheritance diagram is useful for having an overview of how (biological) strings are modelled.
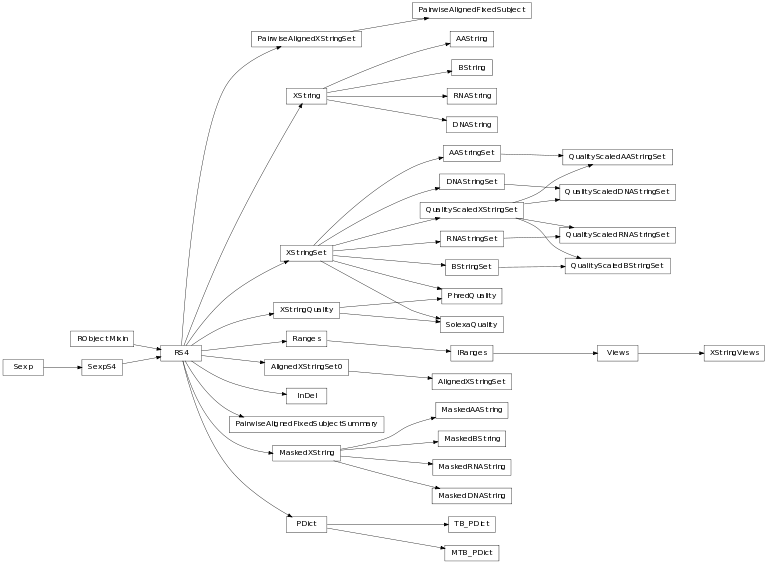
A module to model the Biostrings library in Bioconductor
Copyright 2009-2010 - Laurent Gautier
- class bioc.biostrings.AAString(*args, **kwargs)¶
- classmethod new(x)¶
Parameter: x – a string of amino-acids
- class bioc.biostrings.AlignedXStringSet¶
- class bioc.biostrings.AlignedXStringSet0¶
- alphabet¶
- as_character()¶
- end¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- get_alphabet()¶
- indel()¶
- nchar¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- start¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- unaligned¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- width¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- class bioc.biostrings.BString(*args, **kwargs)¶
Biological string
- classmethod new(x)¶
Parameter: x – a (biological) string
- class bioc.biostrings.DNAString(*args, **kwargs)¶
DNA string
- classmethod new(x)¶
Parameter: x – a DNA string
- reverse_complement()¶
- Return the reverse complement
- class bioc.biostrings.InDel¶
- deletion¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- insertion¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- class bioc.biostrings.MTB_PDict¶
- class bioc.biostrings.MaskedAAString¶
- Masked string of amino-acids
- class bioc.biostrings.MaskedBString¶
- Masked biological string
- class bioc.biostrings.MaskedDNAString¶
- Masked DNA string
- class bioc.biostrings.MaskedRNAString¶
- Masked RNA string
- class bioc.biostrings.MaskedXString¶
“Masked” arbitrary string
- get_masks()¶
- get_unmasked()¶
- Return the strings without its ‘mask’
- masks¶
- Property for both R’s ‘masks’ and ‘masks<-‘
- set_masks(value)¶
- unmasked¶
- Return the strings without its ‘mask’
- class bioc.biostrings.PDict¶
Dictionnary of probes, that is dictionary of of rather short strings.
- count(subject, algorithm='auto', max_mismatch=0, fixed=True, verbose=False)¶
- Count the number of matching subject sequences
- classmethod create_instance(x)¶
Create a preprocessed dictionnary of genomic patterns.
Parameter: x – a string vector, and DNAStringSet, or an XStringViews with s DNAString subject
- match(subject, algorithm='auto', max_mismatch=0, fixed=True, verbose=False)¶
- Match subject sequence(s) to the dictionary
- which(subject, algorithm='auto', max_mismatch=0, fixed=True, verbose=False)¶
- width¶
- class bioc.biostrings.PairwiseAlignedFixedSubject¶
- class bioc.biostrings.PairwiseAlignedFixedSubjectSummary¶
- class bioc.biostrings.PairwiseAlignedXStringSet¶
- static fromCharacter_Character(pattern, target, **kwargs)¶
- static fromCharacter_missing(pattern, **kwargs)¶
- static fromXString_XString(pattern, target, **kwargs)¶
- nchar¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- nindel¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- pattern¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- score¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- class bioc.biostrings.QualityScaledXStringSet¶
- class bioc.biostrings.RNAString(*args, **kwargs)¶
RNA string
- classmethod new(x)¶
Parameter: x – an RNA string
- reverse_complement()¶
- Return the reverse complement
- class bioc.biostrings.TB_PDict¶
‘Trusted-band’ (TB) probe dictionary
- get_tb()¶
- get_tb_width()¶
- tb¶
- tb_width¶
- class bioc.biostrings.XString(*args, **kwargs)¶
Arbitrary string
- alphabet¶
- get_alphabet()¶
- nchar¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- reverse()¶
- class bioc.biostrings.XStringQuality¶
- class bioc.biostrings.XStringViews¶
View on an arbitrary string
- as_matrix(**kwargs)¶
- get_nchar()¶
- nchar¶
- reverse_complement()¶
- Return the reverse and complement for the view
- width¶
- bioc.biostrings.biostrings_conversion(robj)¶
bsgenome: strings information for a complete genome¶
Examples¶
>>> import bioc.bsgenome
>>> genomes = bioc.bsgenome.__rpackage__.available_genomes()
>>> tuple(genomes)
('BSgenome.Amellifera.BeeBase.assembly4',
'BSgenome.Amellifera.UCSC.apiMel2',
'BSgenome.Athaliana.TAIR.01222004',
'BSgenome.Athaliana.TAIR.04232008',
'BSgenome.Btaurus.UCSC.bosTau3',
'BSgenome.Btaurus.UCSC.bosTau4',
'BSgenome.Celegans.UCSC.ce2',
'BSgenome.Cfamiliaris.UCSC.canFam2',
'BSgenome.Dmelanogaster.UCSC.dm2',
'BSgenome.Dmelanogaster.UCSC.dm3',
'BSgenome.Drerio.UCSC.danRer5',
'BSgenome.Ecoli.NCBI.20080805',
'BSgenome.Ggallus.UCSC.galGal3',
'BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg17',
'BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg18',
'BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19',
'BSgenome.Mmusculus.UCSC.mm8',
'BSgenome.Mmusculus.UCSC.mm9',
'BSgenome.Ptroglodytes.UCSC.panTro2',
'BSgenome.Rnorvegicus.UCSC.rn4',
'BSgenome.Scerevisiae.UCSC.sacCer1',
'BSgenome.Scerevisiae.UCSC.sacCer2')
The genome names can be passed to biocLite (see the introduction) for an automagic download and install of the corresponding genome package.
>>> tuple(bioc.bsgenome.__rpackage__.installed_genomes())
('BSgenome.Celegans.UCSC.ce2',
'BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg18',
'BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19')
Installed genomes can be imported, since they are R packages.
>>> from rpy2.robjects.packages import importr
>>> ce2_genome = importr('BSgenome.Celegans.UCSC.ce2')
>>> ce2_genome.Celegans
<BSgenome - Python:0x2a80058 / R:0x4cbdf10>
>>> print(ce2_genome.Celegans.seqlengths)
chrI chrII chrIII chrIV chrV chrX chrM
15080483 15279308 13783313 17493791 20922231 17718849 13794
>>> ce2_genome.Celegans['chrI']
<DNAString - Python:0x2a80878 / R:0x53ac7e4>
Docstrings¶
The class inheritance diagram is useful for having an overview of how the representation of genomes is organized.
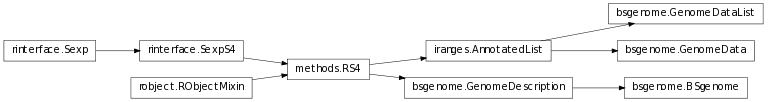
A module to model the BSgenome library in Bioconductor
Copyright 2009 - Laurent Gautier
- class bioc.bsgenome.BSgenome¶
Arbitrary string
- mseqnames¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- seqlengths¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- seqnames¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- class bioc.bsgenome.GenomeData¶
- organism¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- provider¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- provider_version¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- class bioc.bsgenome.GenomeDataList¶
- class bioc.bsgenome.GenomeDescription¶
- organism¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- provider¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- provider_version¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- release_date¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- release_name¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- species¶
- Python representation of an R function such as the character ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ whenever present in the R argument name.
- bioc.bsgenome.bsgenome_conversion(robj)¶