Integration with other tools¶
Triton¶
Triton (http://triton.quarkslab.com/) is a DBA (Dynamic Binary Analysis) framework that can, among other things, create a symbolic equivalent of a set of X86 (32/64) instructions. These symbolic expressions are managed through an AST (Abstract Syntax Tree). More information about Triton’s AST can be found in its documentation.
Arybo can handle a subset of Triton AST to convert it into an MBA variable,
thanks to the arybo.tools.triton2arybo() API. Here is a small example (from
examples/triton_ast.py):
import triton as TT
from arybo.tools import triton2arybo
TT.setArchitecture(TT.ARCH.X86_64)
TT.convertRegisterToSymbolicVariable(TT.REG.RAX)
TT.convertRegisterToSymbolicVariable(TT.REG.RBX)
inst = TT.Instruction()
inst.setOpcodes("\x48\x31\xd8") # xor rax, rbx
TT.processing(inst)
rax_ast = TT.buildSymbolicRegister(TT.REG.RAX)
rax_ast = TT.getFullAst(rax_ast)
print(rax_ast)
e = triton2arybo(rax_ast)
print(e)
Triton needs to be installed. As it only supports Python 2, a Python 2 version of Arybo must be present.
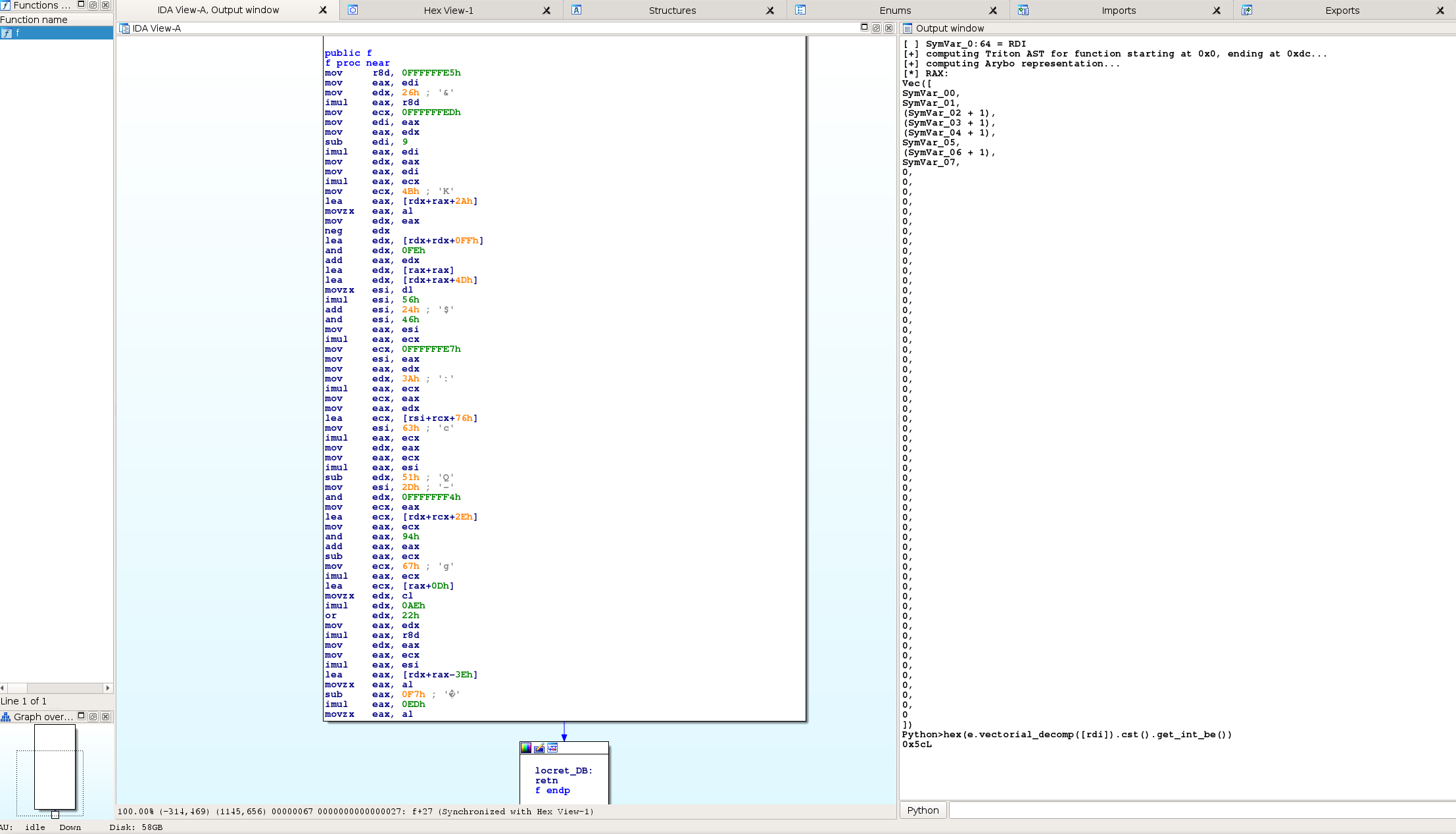
IDA¶
A small POC is provided in the examples/triton_ida.py file that shows how
Triton and Arybo can be used to get the symbolic Arybo representation of a
given x86-64 binary function directly in the IDA disassembler.
This POC has been made for 64-bit system Linux systems. The issue is that IDA uses a 32-bit Python interpreter. The workaround is to use ̀`rpyc` to have Triton and Arybo in a 64-bit process, where IDA stays with its 32-bit process and communication is done through RPC. The overall setup is the following:
- install Arybo and Triton for your 64-bit Linux system for Python 2
- install
rpyc:pip install rpyc - launch the
rpycserver, and make sure it listens on localhost:rpyc_classic.py --host 127.0.0.1 - launch IDA. If you used a virtual environment, you must specify a special
PYTHONPATHthat points to the Python libraries of your virtualenv (for instance:PYTHONPATH=home/user/.virtualenvs/arybo2/lib/python2.7/site-packages)
The script for now assumes that the function has one integer argument and
returns an integer into RAX. Go inside a function, and launch the
example/triton_ida.py script. You will see the Triton and the Arybo output
in the output console. Beware that, has computations are usually done on
32/64-bit registers, this can take a quite bit of time! Further work is going
on to improve the performances of this overall process.
Here is on example on a C version of the example/xor_5C.py function:
There is also ongoing work to make a more user-friendly and generic IDA plugin. Feel free to contact us if you’re interested!