Target definitions.
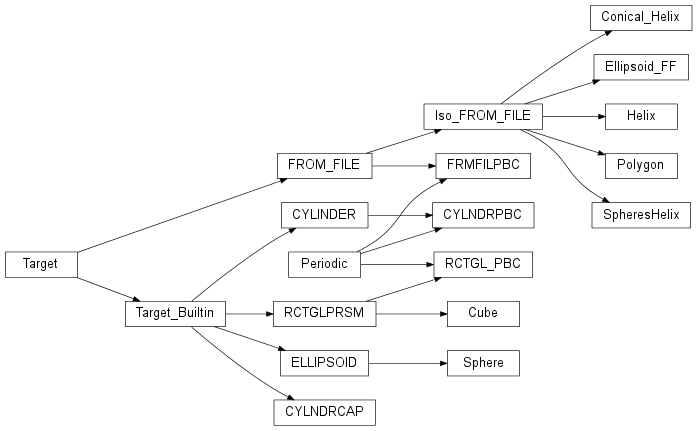
Otherclasses derive from these. Generally not intended to be used on their own.
| Target([directive, sh_param, material, ...]) | The base class for defining DDscat Target geometries. |
| Target_Builtin(directive[, d, material, folder]) | Base class for the standard target geometries that are built into DDSCAT. |
| Periodic | Base class for periodic targets |
Classes for defining isolated finite targets based on target definitions built into DDSCAT.
| Target_Builtin(directive[, d, material, folder]) | Base class for the standard target geometries that are built into DDSCAT. |
| RCTGLPRSM(phys_shape[, d, material, folder]) | A rectangular prism target |
| CYLNDRCAP(length, radius[, d, material, folder]) | Homogeneous, isotropic finite cylinder with hemispherical endcaps. |
| ELLIPSOID(semiaxes[, d, material, folder]) | An Ellipsoid target |
| CYLINDER(length, radius, orient[, d, ...]) | Homogeneous, isotropic finite cylinder |
| Sphere(radius[, d, material, folder]) | A Sphere target. |
| Cube(length[, d, material, folder]) | A Cube target. |
Classes for defining isolated finite targets of arbitrary shape.
| FROM_FILE([grid, d, material, folder]) | Base class for targets of arbitrary geometry. |
| FRMFILPBC([grid, period, d, material, ...]) | Base class for periodic targets of arbitrary geometry. |
| Iso_FROM_FILE([grid, d, material, folder]) | Base class for targets of arbitrary geometry with isotropic materials. |
| Ellipsoid_FF(semiaxes[, d, material, folder]) | Build an ellipsoidal target to be loaded from file |
| Helix(height, pitch, major_r, minor_r[, d, ...]) | A helix target. |
| SpheresHelix(height, pitch, major_r, ...[, ...]) | A helix target composed of isolated spheres |
| Conical_Helix(height, pitch1, pitch2, ...[, ...]) | A helix target |
Classes for defining targets with 1D and 2D semi-infinite periodicity.
| Periodic | Base class for periodic targets |
| FRMFILPBC([grid, period, d, material, ...]) | Base class for periodic targets of arbitrary geometry. |
| RCTGL_PBC(phys_shape, period[, d, material, ...]) | A target of periodic rectangular prisms. |
| CYLNDRPBC(length, radius, orient, period[, ...]) | A target of periodic cylinders. |
Target definitions.
Default spacing between dipoles (in um)
Bases: object
The base class for defining DDscat Target geometries.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
As it is, this class creates generic targets, which contain only a directive, sh_param, material and aeff: the bare minimum necessary to write a ddscat.par file. It is intended to provide an interface as close as possible to bare DDSCAT target definitions. It uses dipole units rather than subclasses which should use physical units.
Typically, this class will be subclassed to create more useful and feature- rich targets. Derived classes must provide the following attributes and methods: * sh_param: A property that returns the three values of the SHPAR definition used by DDSCAT * _calc_N(): A static method to calculate the number of dipoles based on the shape parameters * fromfile(): A class method to generate a working object from a ddscat.par file
Bases: ScatPy.targets.Target
Base class for the standard target geometries that are built into DDSCAT.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Typically, this class will be subclassed to create more useful and feature- rich targets. Classes should take their names from the name used by DDSCAT (e.g. RCTGLPRSM, ELLIPSOID).
Target subclasses constructed with :class:Target_Builtin are intended to work with physical units rather than dipole units used in :class:Target. Therefore, derived classes must provide the following attributes and methods for converting between physical dimensions and the internal representation understood by DDSCAT: * sh_param: A property that returns the three values of the SHPAR definition used by DDSCAT * _calc_N(): A static method to calculate the number of dipoles based on the shape parameters * fromfile(): A class method to generate a working object from a ddscat.par file
Unimplemented method for calculating the shape parameters.
Subclasses must implement this themselves. The method should take the internally stored physical dimensions (e.g. self.radius, self.length) and translate them into the shape parameters DDSCAT expects for this target type.
This would be a good application for ABCs.
Unimplemented method for loading target from file.
Subclasses must implement this themselves. The form is to load the target information from the par file using _read_values(). Then parse those values and pass them to the class’s initializer.
This would be a good application for ABCs.
Bases: ScatPy.targets.Target_Builtin
A rectangular prism target
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Bases: ScatPy.targets.RCTGLPRSM
A Cube target.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Bases: ScatPy.targets.Target_Builtin
Homogeneous, isotropic finite cylinder with hemispherical endcaps.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Total height of the structureis length+2*rad
Bases: ScatPy.targets.Target_Builtin
An Ellipsoid target
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Bases: ScatPy.targets.ELLIPSOID
A Sphere target.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Bases: ScatPy.targets.Target_Builtin
Homogeneous, isotropic finite cylinder
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Bases: ScatPy.targets.Target
Base class for targets of arbitrary geometry.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
If anisotropic, the “microcrystals” in the target are assumed to be aligned with the principal axes of the dielectric tensor parallel to the TF axes.
FROM_FILE does not inherit from Target_Builtin so for the purposes of inheritence it is not considered a builtin target.
Load target definition from the specified .par file.
Assumes that the accompanying shape.dat file is in the same folder.
This function currently assumes that the target basis vectors are orthonormal.
Generate a target from a function.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
See numpy.fronfunction for details on the function func.
Bases: ScatPy.targets.FROM_FILE
Base class for targets of arbitrary geometry with isotropic materials.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
The major difference is that the grid in this case has only one value at each dipole.
Bases: ScatPy.targets.Iso_FROM_FILE
Build an ellipsoidal target to be loaded from file
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Bases: ScatPy.targets.Iso_FROM_FILE
A helix target.
dimensions are physical, in um
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Bases: ScatPy.targets.Iso_FROM_FILE
A helix target composed of isolated spheres
Dimensions are physical, in um.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Bases: ScatPy.targets.Iso_FROM_FILE
A helix target
dimensions are physical, in um
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Bases: ScatPy.targets.Iso_FROM_FILE
A planar target in the shape defined by the polygon
dimensions are physical, in um
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Dipoles within the polygon correspond to material, outside to ambient.
Bases: object
Base class for periodic targets
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Bases: ScatPy.targets.FROM_FILE, ScatPy.targets.Periodic
Base class for periodic targets of arbitrary geometry.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
If anisotropic, the “microcrystals” in the target are assumed to be aligned with the principal axes of the dielectric tensor parallel to the TF axes.
FROMFILPBC does not inherit from Target_Builtin so for the purposes of inheritence it is not considered a builtin target.
Bases: ScatPy.targets.RCTGLPRSM, ScatPy.targets.Periodic
A target of periodic rectangular prisms.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
Bases: ScatPy.targets.CYLINDER, ScatPy.targets.Periodic
A target of periodic cylinders.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
A dict which translates between a finite isolated target class and its corresponding (semi)infite periodic partner. The keys are the classes of the isolated target, and the values are the classes of the periodic ones.
Punches holes into a target
radius: the radius of the holes to be punched (in units of d)
Where to punch the holes can be specified by:
posns: a list of the x,y,z positions to punch the holes
or
num: the number of holes. their positions are selected randomly seed: a seed value to use for the random number generator