Pyvot workflows¶
Pyvot aims to enable both standalone Excel automation and interactive experimentation / analysis. Some users simply want to xl.tools.map() an Excel column once-off, while others need a repeatable transformation to be applied to future workbooks.
Interactive usage and xl.shell¶
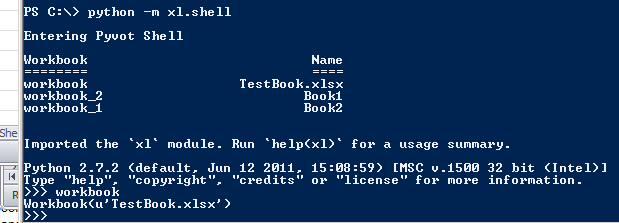
Pyvot provides a customized interactive shell to get running quickly:
python -m xl.shell
The shell mimics the normal Python REPL, but performs additional set-up for convenient usage of Pyvot:
- xl is imported
- An empty Excel workbook is opened, if no others are present
- Open Excel workbooks are assigned variables (workbook, workbook_1, etc.). Each such variable and its workbook’s name are printed in a table
Standalone usage for repeatable transforms¶
As a regular Python module, Pyvot can also be used from standalone scripts. This is useful for creating repeatable (and distributable) transformations, with familiar program structure:
python summarize_sales.py --by-region \\share\sales_9-30-2011.xlsx
Code assets born in the interactive shell transfer easily to scripts. Needed changes in the transition on using Workbooks and Ranges explicitly:
- Prefer xl.sheet.Workbook.get() to xl.tools.get(). The user may have other workbooks open
- Pass the desired absolute file path to the Workbook constructor. This will open the workbook if needed, or connect to an existing instance.
- Prefer table column names to A1-style references
- Don’t assume that mapping “NumSales” writes to column B; use the return value of xl.map (similarly for other functions)
Usage with Python Tools for Visual Studio¶
Whether using the Pyvot interactive shell or standalone model, Python Tools for Visual Studio (PTVS) provides a convenient development environment.
In interactive usage, the “Send to interactive window” command allows iterative, interactive development of functions and snippets that operate on an open workbook. This solves the common pain of modifying a function defined within a REPL session. IntelliSense within the REPL eases discovery of the Pyvot API.
In standalone usage and development, IntelliSense provides quick access to the Pyvot API and documentation. The VS debugger enables stepping through a Pyvot program (seeing the workbook update in Excel each step of the way).