The Arguments¶
"""APE (the all-purpose-evaluator)
Usage: ape -h | -v
ape [--debug|--silent] [--pudb|--pdb] <command> [<argument>...]
ape [--debug|--silent] [--trace|--callgraph] <command> [<argument>...]
Help Options:
-h, --help Display this help message and quit.
-v, --version Display the version number and quit.
Logging Options:
--debug Set logging level to DEBUG.
--silent Set logging level to ERROR.
Debugging Options:
--pudb Enable the `pudb` debugger (if installed)
--pdb Enable the `pdb` (python's default) debugger
--trace Enable code-tracing
--callgraph Create a call-graph of for the code
Positional Arguments:
<command> The name of a sub-command (see below)
<argument>... One or more options or arguments for the sub-command
Available Sub-Commands:
run Run a plugin
fetch Fetch a sample configuration-file
help Display more help
list List known plugins
check Check a configuration
To get help for a sub-command pass `-h` as the argument. e.g.:
ape run -h
"""
Contents:
The ArgumentConstants¶
class ArgumentsConstants(object):
"""
Constants for the arguments
"""
__slots__ = ()
debug = "--debug"
silent = '--silent'
pudb = "--pudb"
pdb = '--pdb'
trace = '--trace'
callgraph = '--callgraph'
command = "<command>"
argument = '<argument>'
# end ArgumentConstants
The BaseArguments¶
This is the base-class for the newer docopt-based arguments. See the developer documentation for a more detailed explanation of what’s going on. As a transitional feature, the BaseArgument class definition holds an instance of the UbootKommandant so that its children can access it.
| docopt(doc[, argv, help, version, options_first]) | Parse argv based on command-line interface described in doc. |
| DocoptExit([message]) | Exit in case user invoked program with incorrect arguments. |
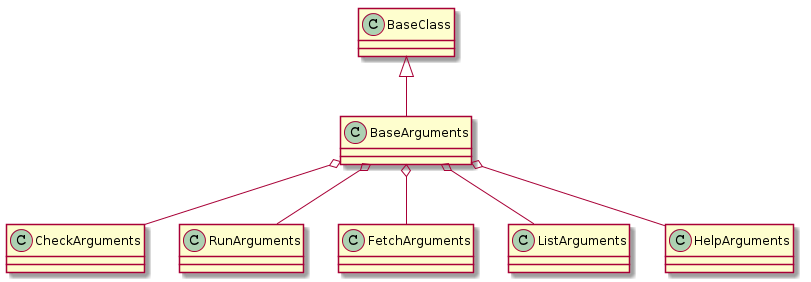
| BaseArguments | |
| BaseArguments.arguments | |
| BaseArguments.sub_arguments | |
| BaseArguments.debug | |
| BaseArguments.silent | |
| BaseArguments.pudb | |
| BaseArguments.pdb | |
| BaseArguments.trace | |
| BaseArguments.callgraph | |
| BaseArguments.reset |