pyqode.core.api package¶
Module content¶
This package contains the bases classes of pyqode and some utility functions.
Classes¶
CodeEdit¶
- class pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit(parent=None, create_default_actions=True)¶
Bases: PyQt5.QtWidgets.QPlainTextEdit
The editor widget is a simple extension to QPlainTextEdit.
It adds a few utility signals/methods and introduces the concepts of Managers, Modes and Panels.
A mode/panel is an editor extension that, once added to a CodeEdit instance, may modify its behaviour and appearance:
Modes are simple objects which connect to the editor signals to append new behaviours (such as automatic indentation, code completion, syntax checking,...)
Panels are the combination of a Mode and a QWidget. They are displayed in the CodeEdit’s content margins.
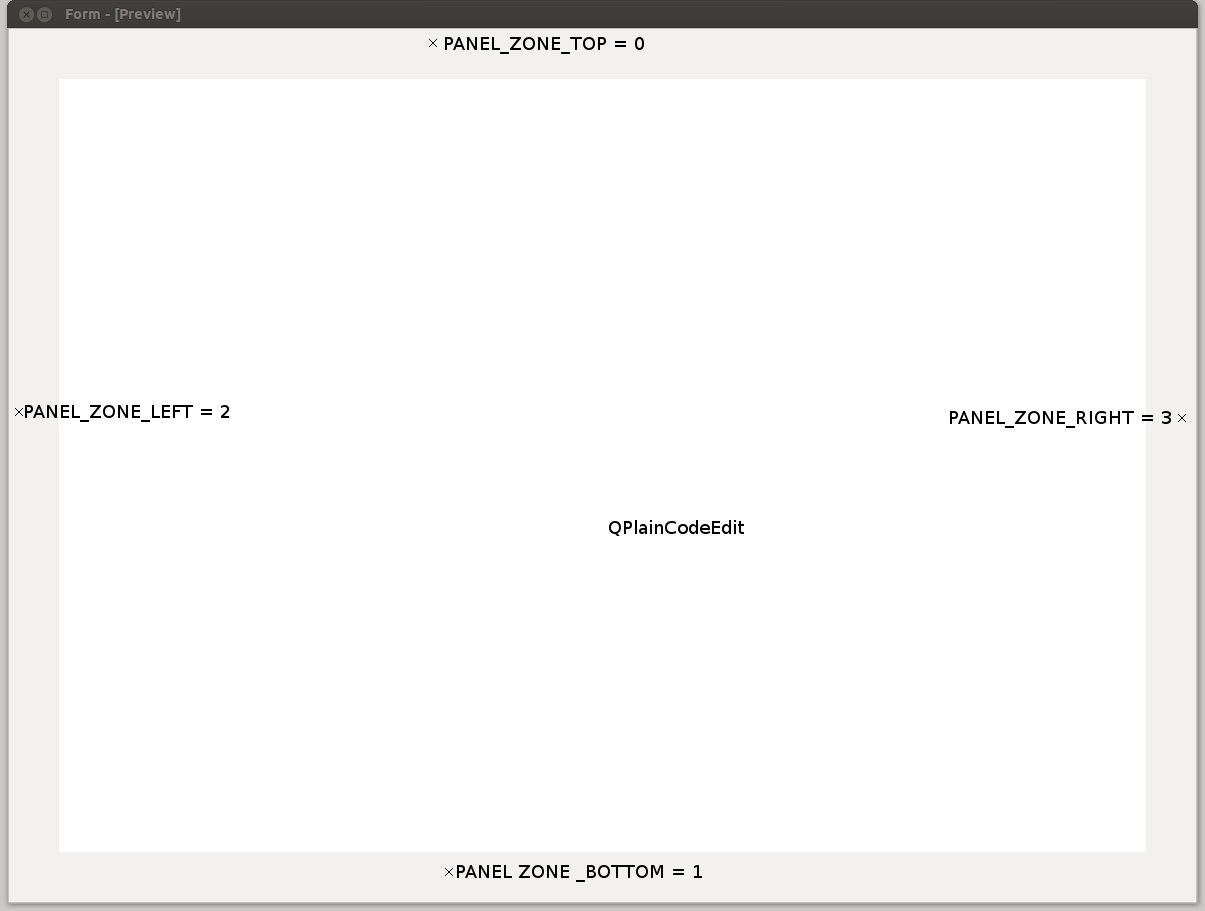
When you install a Panel on a CodeEdit, you can choose to install it in one of the four following zones:
A manager is an object that literally manage a specific aspect of pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit. There are managers to manage the list of modes/panels, to open/save file and to control the backend:
- pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit.file:
File manager. Use it to open/save files or access the opened file attribute.
- pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit.backend:
Backend manager. Use it to start/stop the backend or send a work request.
- pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit.modes:
Modes manager. Use it to append/remove modes on the editor.
- pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit.panels:
Modes manager. Use it to append/remove panels on the editor.
Starting from version 2.1, CodeEdit defines the pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit.mimetypes class attribute that can be used by IDE to determine which editor to use for a given mime type. This property is a list of supported mimetypes. An empty list means the CodeEdit is generic. Code editors specialised for a specific language should define the mime types they support!
- actions()¶
Returns the list of actions/sepqrators of the context menu.
- add_action(action)¶
Adds an action to the editor’s context menu.
Parameters: action – QtWidgets.QAction
Adds a sub-menu to the editor context menu.
Menu are put at the bottom of the context menu.
Note
to add a menu in the middle of the context menu, you can always add its menuAction().
Parameters: menu – menu to add
- add_separator()¶
Adds a sepqrator to the editor’s context menu.
Returns: The sepator that has been added. Return type: QtWidgets.QAction
- clone()¶
Clone ourselves, return an instance of the same class, using the default QWidget constructor.
- close(clear=True)¶
Closes the editor, stops the backend and removes any installed mode/panel.
This is also where we cache the cursor position.
Parameters: clear – True to clear the editor content before closing.
- delete()¶
Deletes the selected text
- duplicate_line()¶
Duplicates the line under the cursor. If multiple lines are selected, only the last one is duplicated.
- focusInEvent(event)¶
Overrides focusInEvent to emits the focused_in signal
Parameters: event – QFocusEvent
- focusOutEvent(event)¶
Gets the editor context menu.
Returns: QMenu
- goto_line()¶
Shows the go to line dialog and go to the selected line.
- indent()¶
Indents the text cursor or the selection.
Emits the pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit.indent_requested signal, the pyqode.core.modes.IndenterMode will perform the actual indentation.
- insert_action(action, prev_action)¶
Inserts an action to the editor’s context menu
Parameters: - action – action to insert
- prev_action – the action after which the new action must be inserted
- keyPressEvent(event)¶
Overrides the keyPressEvent to emit the key_pressed signal.
Also takes care of indenting and handling smarter home key.
Parameters: event – QKeyEvent
- keyReleaseEvent(event)¶
Overrides keyReleaseEvent to emit the key_released signal.
Parameters: event – QKeyEvent
- link(clone)¶
Links the clone with its original. We copy the file manager infos (path, mimetype, ...) and setup the clone text document as reference to our text document.
Parameters: clone – clone to link.
- mouseDoubleClickEvent(event)¶
- mouseMoveEvent(event)¶
Overrides mouseMovedEvent to display any decoration tooltip and emits the mouse_moved event.
Parameters: event – QMouseEvent
- mousePressEvent(event)¶
Overrides mousePressEvent to emits mouse_pressed signal
Parameters: event – QMouseEvent
- mouseReleaseEvent(event)¶
Emits mouse_released signal.
Parameters: event – QMouseEvent
- paintEvent(e)¶
Overrides paint event to update the list of visible blocks and emit the painted event.
Parameters: e – paint event
- rehighlight()¶
Calls rehighlight on the installed syntax highlighter mode.
- remove_action(action)¶
Removes an action/separator from the editor’s context menu.
Parameters: action – Action/seprator to remove.
Removes a sub-menu from the context menu. :param menu: Sub-menu to remove.
- reset_zoom()¶
Resets the zoom level.
- resizeEvent(e)¶
Overrides resize event to resize the editor’s panels.
Parameters: e – resize event
- setPlainText(txt, mime_type, encoding)¶
Extends setPlainText to force the user to setup an encoding and a mime type.
Emits the new_text_set signal.
Parameters: - txt – The new text to set.
- mime_type – Associated mimetype. Setting the mime will update the pygments lexer.
- encoding – text encoding
- set_mouse_cursor(cursor)¶
Changes the viewport’s cursor
Parameters: cursor (QtWidgets.QCursor) – the mouse cursor to set.
- showEvent(event)¶
Overrides showEvent to update the viewport margins
- show_tooltip(pos, tooltip, _sender_deco=None)¶
Show a tool tip at the specified position
Parameters: - pos – Tooltip position
- tooltip – Tooltip text
- _sender_deco – TextDecoration which is the sender of the show tooltip request. (for internal use only).
- split()¶
Split the code editor widget, return a clone of the widget ready to be used (and synchronised with its original).
- Splitting the widget is done in 2 steps:
first we clone the widget, you can override clone if your widget needs additional arguments.
- then we link the two text document and disable some modes on the
cloned instance (such as the watcher mode).
- un_indent()¶
Un-indents the text cursor or the selection.
Emits the pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit.unindent_requested signal, the pyqode.core.modes.IndenterMode will perform the actual un-indentation.
- wheelEvent(event)¶
Emits the mouse_wheel_activated signal.
Parameters: event – QMouseEvent
- zoom_in(increment=1)¶
Zooms in the editor (makes the font bigger).
Parameters: increment – zoom level increment. Default is 1.
- zoom_out(decrement=1)¶
Zooms out the editor (makes the font smaller).
Parameters: decrement – zoom level decrement. Default is 1. The value is given as an absolute value.
- backend¶
Returns a reference to the pyqode.core.managers.BackendManager used to control the backend process.
- background¶
The editor background color (QColor)
- decorations¶
Returns a reference to the pyqode.core.managers.TextDecorationManager used to manage the list of pyqode.core.api.TextDecoration
- dirty¶
Tells whethere the content of editor has been modified.
(this is just a shortcut to QTextDocument.isModified
Type: bool
- dirty_changed¶
Signal emitted when the dirty state changed
- file¶
Returns a reference to the pyqode.core.managers.FileManager used to open/save file on the editor
- focused_in¶
Signal emitted when focusInEvent is is called
- font_name¶
The editor font family name.
- font_size¶
The font point size.
Note
Please, never use setFontPointSize/setFontFamily functions directly as the values you define there will be overwritten as soon as the user zoom the editor or as soon as a stylesheet property has changed.
- foreground¶
The editor foreground color (QColor)
- indent_requested¶
Signal emitted when the user press the TAB key
- key_pressed¶
Signal emitted when a key is pressed
- key_released¶
Signal emitted when a key is released
- mimetypes = []¶
Store the list of mimetypes associated with the editor, for specialised editors.
- modes¶
Returns a reference to the pyqode.core.managers.ModesManager used to manage the collection of installed modes.
- mouse_double_clicked¶
Signal emitted when a mouse double click event occured
- mouse_moved¶
Signal emitted when the mouse_moved
- mouse_pressed¶
Signal emitted when a mouse button is pressed
- mouse_released¶
Signal emitted when a mouse button is released
- mouse_wheel_activated¶
Signal emitted on a wheel event
- new_text_set¶
Signal emitted when a new text is set on the widget
- painted¶
Paint hook
- panels¶
Returns a reference to the pyqode.core.managers.PanelsManager used to manage the collection of installed panels
- post_key_pressed¶
Signal emitted at the end of the key_pressed event
- save_on_focus_out¶
Automatically saves editor content on focus out.
Default is False.
- selection_background¶
The editor selection’s background color.
- selection_foreground¶
The editor selection’s foreground color.
- show_whitespaces¶
Shows/Hides virtual white spaces.
- syntax_highlighter¶
Returns a reference to the syntax highlighter mode currently used to highlight the editor content.
Returns: pyqode.core.api.SyntaxHighlighter
- tab_length¶
Tab length, number of spaces.
- text_saved¶
Signal emitted when the text is saved to file
- text_saving¶
Signal emitted before the text is saved to file
- unindent_requested¶
Signal emitted when the user press the BACK-TAB (Shift+TAB) key
- use_spaces_instead_of_tabs¶
Use spaces instead of tabulations. Default is True.
- visible_blocks¶
Returns the list of visible blocks.
Each element in the list is a tuple made up of the line top position, the line number and the QTextBlock itself.
Returns: A list of tuple(top_position, line_number, block) Return type: List of tuple(int, int, QtWidgets.QTextBlock)
- whitespaces_foreground¶
The editor white spaces’ foreground color. White spaces are highlighted by the syntax highlighter. You should call rehighlight to update their color. This is not done automatically to prevent multiple, useless call to rehighlight which can take some time on big files.
- word_separators¶
The list of word separators used by the code completion mode and the word clicked mode.
- zoom_level¶
Gets/Sets the editor zoom level.
The zoom level is a value that is added to the current editor font size. Negative values are used to zoom out the editor, positive values are used to zoom in the editor.
ColorScheme¶
- class pyqode.core.api.ColorScheme(style)¶
Bases: builtins.object
Translates a pygments style into a dictionary of colors associated with a style key.
See pyqode.core.api.syntax_highligter.COLOR_SCHEM_KEYS for the available keys.
- background¶
Gets the background color. :return:
- formats = None¶
Dictionary of formats colors (keys are the same as for pyqode.core.api.COLOR_SCHEME_KEYS
- highlight¶
Gets the highlight color. :return:
- name¶
Name of the color scheme, this is usually the name of the associated pygments style.
DelayJobRunner¶
- class pyqode.core.api.DelayJobRunner(delay=500)¶
Bases: builtins.object
Utility class for running job after a certain delay. If a new request is made during this delay, the previous request is dropped and the timer is restarted for the new request.
We use this to implement a cooldown effect that prevents jobs from being executed while the IDE is not idle.
A job is a simple callable.
- cancel_requests()¶
Cancels pending requests.
FoldDetector¶
- class pyqode.core.api.FoldDetector¶
Bases: builtins.object
Base class for fold detectors.
A fold detector takes care of detecting the text blocks fold levels that are used by the FoldingPanel to render the document outline.
To use a FoldDetector, simply set it on a syntax_highlighter:
editor.syntax_highlighter.fold_detector = my_fold_detector
- detect_fold_level(prev_block, block)¶
Detects the block fold level.
The default implementation is based on the block indentation.
Note
Blocks fold level must be contiguous, there cannot be a difference greater than 1 between two successive block fold levels.
Parameters: - prev_block – first previous non-blank block or None if this is the first line of the document
- block – The block to process.
Returns: Fold level
- process_block(current_block, previous_block, text)¶
Processes a block and setup its folding info.
This method call detect_fold_level and handles most of the tricky corner cases so that all you have to do is focus on getting the proper fold level foreach meaningful block, skipping the blank ones.
Parameters: - current_block – current block to process
- previous_block – previous block
- text – current block text
- editor = None¶
Reference to the parent editor, automatically set by the syntax highlighter before process any block.
- limit = None¶
Fold level limit, any level greater or equal is skipped. Default is sys.maxsize (i.e. all levels are accepted)
FoldScope¶
- class pyqode.core.api.FoldScope(block)¶
Bases: builtins.object
Utility class for manipulating fold-able code scope (fold/unfold, get range, child and parent scopes and so on).
A scope is built from a fold trigger (QTextBlock).
- blocks(ignore_blank_lines=True)¶
This generator generates the list of blocks directly under the fold region. This list does not contain blocks from child regions.
Parameters: ignore_blank_lines – True to ignore last blank lines.
- child_regions()¶
This generator generates the list of direct child regions.
- static find_parent_scope(block)¶
Find parent scope, if the block is not a fold trigger.
Parameters: block – block from which the research will start
- fold()¶
Folds the region.
- get_range(ignore_blank_lines=True)¶
Gets the fold region range (start and end line).
Note
Start line do no encompass the trigger line.
Parameters: ignore_blank_lines – True to ignore blank lines at the end of the scope (the method will rewind to find that last meaningful block that is part of the fold scope). Returns: tuple(int, int)
- parent()¶
Return the parent scope.
Returns: FoldScope or None
- text(max_lines=9223372036854775807)¶
Get the scope text, with a possible maximum number of lines.
Parameters: max_lines – limit the number of lines returned to a maximum. Returns: str
- unfold()¶
Unfolds the region.
- collapsed¶
Returns True if the block is collasped, False if it is expanded.
- scope_level¶
Returns the fold level of the first block of the foldable scope ( just after the trigger)
Returns:
- trigger_level¶
Returns the fold level of the block trigger :return:
IndentFoldDetector¶
- class pyqode.core.api.IndentFoldDetector¶
Bases: pyqode.core.api.folding.FoldDetector
Simple fold detector based on the line indentation level
- detect_fold_level(prev_block, block)¶
Detects fold level by looking at the block indentation.
Parameters: - prev_block – previous text block
- block – current block to highlight
Manager¶
- class pyqode.core.api.Manager(editor)¶
Bases: builtins.object
- A manager manages a specific aspect of a CodeEdit instance:
- backend management (start/stop server, request work,...)
- modes management
- panels management and drawing
- file manager
Managers are typically created internally when you create a CodeEdit. You interact with them later, e.g. when you want to start the backend process or when you want to install/retrieve a mode or a panel.
- ::
editor = CodeEdit()
# use the backend manager to start the backend server editor.backend.start(...) editor.backend.send_request(...)
# use the panels controller to install a panel editor.panels.install(MyPanel(), MyPanel.Position.Right) my_panel = editor.panels.get(MyPanel)
# and so on
- editor¶
Return a reference to the parent code edit widget.
Mode¶
- class pyqode.core.api.Mode¶
Bases: builtins.object
Base class for editor extensions. An extension is a “thing” that can be installed on an editor to add new behaviours or to modify its appearance.
A mode is added to an editor by using the ModesManager/PanelsManager:
- pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit.modes.append() or
- pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit.panels.append()
Subclasses may/should override the following methods:
..warning: The mode will be identified by its class name, this means that there cannot be two modes of the same type on the same editor instance!
- clone_settings(original)¶
Clone the settings from another mode (same class).
This method is called when splitting an editor widget.
Parameters: original – other mode (must be the same class). Note
The base method does not do anything, you must implement this method for every new mode/panel (if you plan on using the split feature). You should also make sure any properties will be propagated to the clones.
- on_install(editor)¶
Installs the extension on the editor.
Parameters: editor (pyqode.core.api.code_edit.CodeEdit) – editor widget instance Note
This method is called by editor when you install a Mode. You should never call it yourself, even in a subclasss.
Warning
Don’t forget to call super when subclassing
- on_state_changed(state)¶
Called when the enable state has changed.
This method does not do anything, you may override it if you need to connect/disconnect to the editor’s signals (connect when state is true and disconnect when it is false).
Parameters: state (bool) – True = enabled, False = disabled
- on_uninstall()¶
Uninstalls the mode from the editor.
- description = None¶
Mode description
- editor¶
Returns a reference to the parent editor widget.
READ ONLY
Return type: pyqode.core.api.code_edit.CodeEdit
- enabled¶
Tells if the mode is enabled, pyqode.core.api.Mode.on_state_changed() will be called as soon as the mode state changed.
Type: bool
- name = None¶
Mode name/identifier. pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit uses
Panel¶
- class pyqode.core.api.Panel¶
Bases: PyQt5.QtWidgets.QWidget, pyqode.core.api.mode.Mode
Base class for editor panels.
A panel is a mode and a QWidget.
Note
Use enabled to disable panel actions and setVisible to change the visibility of the panel.
- class Position¶
Bases: builtins.object
Enumerates the possible panel positions
- classmethod iterable()¶
Returns possible positions as an iterable (list)
- BOTTOM = 3¶
Bottom margin
- LEFT = 1¶
Left margin
- RIGHT = 2¶
Right margin
- TOP = 0¶
Top margin
- Panel.on_install(editor)¶
Extends pyqode.core.api.Mode.on_install() method to set the editor instance as the parent widget.
Warning
Don’t forget to call super if you override this method!
Parameters: editor (pyqode.core.api.CodeEdit) – editor instance
- Panel.paintEvent(event)¶
- Panel.setVisible(visible)¶
Shows/Hides the panel
Automatically call CodeEdit.refresh_panels.
Parameters: visible – Visible state
- Panel.order_in_zone = None¶
Panel order into the zone it is installed to. This value is automatically set when installing the panel but it can be changed later (negative values can also be used).
- Panel.position = None¶
Position in the editor (top, left, right, bottom)
- Panel.scrollable¶
A scrollable panel will follow the editor’s scroll-bars. Left and right panels follow the vertical scrollbar. Top and bottom panels follow the horizontal scrollbar.
Type: bool
SyntaxHighlighter¶
- class pyqode.core.api.SyntaxHighlighter(parent, color_scheme=None)¶
Bases: PyQt5.QtGui.QSyntaxHighlighter, pyqode.core.api.mode.Mode
Abstract base class for syntax highlighter modes.
It fills up the document with our custom block data (fold levels, triggers,...).
It does not do any syntax highlighting, that task is left to sublasses such as pyqode.core.modes.PygmentsSyntaxHighlighter.
Subclasses must override the pyqode.core.api.SyntaxHighlighter.highlight_block() method to apply custom highlighting.
Note
Since version 2.1 and for performance reasons, we store all our data in the block user state as a bit-mask. You should always use pyqode.core.api.TextBlockHelper to retrieve or modify those data.
- clone_settings(original)¶
- highlightBlock(text)¶
Highlights a block of text. Please do not override, this method. Instead you should implement pyqode.core.api.SyntaxHighlighter.highlight_block().
Parameters: text – text to highlight.
- highlight_block(text, block)¶
Abstract method. Override this to apply syntax highlighting.
Parameters: - text – Line of text to highlight.
- block – current block
- on_install(editor)¶
- refresh_editor(color_scheme)¶
Refresh editor settings (background and highlight colors) when color scheme changed.
Parameters: color_scheme – new color scheme.
- rehighlight()¶
Rehighlight the entire document, may be slow.
- block_highlight_finished¶
Signal emitted at the end of highlightBlock. Parameters are the highlighter instance and the current text block
- block_highlight_started¶
Signal emitted at the start of highlightBlock. Parameters are the highlighter instance and the current text block
- color_scheme¶
Returns a reference to the current color scheme.
- fold_detector = None¶
Fold detector. Set it to a valid FoldDetector to get code folding to work. Default is None
- formats¶
Returns the color shcme formats dict.
TextBlockHelper¶
- class pyqode.core.api.TextBlockHelper¶
Bases: builtins.object
Helps retrieving the various part of the user state bitmask.
This helper should be used to replace calls to QTextBlock.setUserState/QTextBlock.getUserState as well as QSyntaxHighlighter.setCurrentBlockState/ QSyntaxHighlighter.currentBlockState and QSyntaxHighlighter.previousBlockState.
The bitmask is made up of the following fields:
- bit0 -> bit26: User state (for syntax highlighting)
- bit26: fold trigger state
- bit27-bit29: fold level (8 level max)
- bit30: fold trigger flag
- bit0 -> bit15: 16 bits for syntax highlighter user state ( for syntax highlighting)
- bit16-bit25: 10 bits for the fold level (1024 levels)
- bit26: 1 bit for the fold trigger flag (trigger or not trigger)
- bit27: 1 bit for the fold trigger state (expanded/collapsed)
- static get_fold_lvl(block)¶
Gets the block fold level
Parameters: block – block to access. Returns: The block fold level
- static get_fold_trigger_state(block)¶
Gets the fold trigger state.
Parameters: block – QTextBlock Returns: False for an open trigger, True for for closed trigger
- static get_state(block)¶
Gets the user state, generally used for syntax highlighting. :param block: block to access :return: The block state
- static is_fold_trigger(block)¶
Checks if the block is a fold trigger.
Parameters: block – block to check Returns: True if the block is a fold trigger (represented as a node in the fold panel)
- static set_fold_lvl(block, val)¶
Sets the block fold level.
Parameters: - block – block to modify
- val – The new fold level [0-7]
- static set_fold_trigger(block, val)¶
Set the block fold trigger flag (True means the block is a fold trigger).
Parameters: - block – block to set
- val – value to set
- static set_fold_trigger_state(block, val)¶
Sets the fold trigger state.
Parameters: - block – The block to modify
- val – The new trigger state (False = open, True = closed)
- static set_state(block, state)¶
Sets the user state, generally used for syntax highlighting.
Parameters: - block – block to modify
- state – new state value.
Returns:
TextBlockUserData¶
TextDecoration¶
- class pyqode.core.api.TextDecoration(cursor_or_bloc_or_doc, start_pos=None, end_pos=None, start_line=None, end_line=None, draw_order=0, tooltip=None, full_width=False)¶
Bases: PyQt5.QtWidgets.ExtraSelection
Helper class to quickly create a text decoration. The text decoration is an utility class that adds a few utility methods to QTextEdit.ExtraSelection.
In addition to the helper methods, a tooltip can be added to a decoration. (useful for errors markers and so on...)
- Text decoration expose a clicked signal stored in a separate QObject:
- pyqode.core.api.TextDecoration.Signals
deco = TextDecoration() deco.signals.clicked.connect(a_slot) def a_slot(decoration): print(decoration)
- class Signals¶
Bases: PyQt5.QtCore.QObject
Holds the signals for a TextDecoration (since we cannot make it a QObject, we need to store its signals in an external QObject).
- clicked¶
Signal emitted when a TextDecoration has been clicked.
- TextDecoration.contains_cursor(cursor)¶
Checks if the textCursor is in the decoration
Parameters: cursor (QtGui.QTextCursor) – The text cursor to test Returns: True if the cursor is over the selection
- TextDecoration.select_line()¶
Select the entire line but starts at the first non whitespace character and stops at the non-whitespace character. :return:
- TextDecoration.set_as_bold()¶
Uses bold text
- TextDecoration.set_as_error(color=7)¶
Highlights text as a syntax error.
Parameters: color (QtGui.QColor) – Underline color
- TextDecoration.set_as_spell_check(color=9)¶
Underlines text as a spellcheck error.
Parameters: color (QtGui.QColor) – Underline color
- TextDecoration.set_as_underlined(color=9)¶
Underlines the text
Parameters: color – underline color.
- TextDecoration.set_as_warning(color=<PyQt5.QtGui.QColor object at 0x7fa4e2520d68>)¶
Highlights text as a syntax warning
Parameters: color (QtGui.QColor) – Underline color
- TextDecoration.set_background(brush)¶
Sets the background brush.
Parameters: brush (QtGui.QBrush) – Brush
- TextDecoration.set_foreground(color)¶
Sets the foreground color. :param color: Color :type color: QtGui.QColor
- TextDecoration.set_full_width(flag=True, clear=True)¶
Enables FullWidthSelection (the selection does not stops at after the character instead it goes up to the right side of the widget).
Parameters:
- TextDecoration.set_outline(color)¶
Uses an outline rectangle.
Parameters: color (QtGui.QColor) – Color of the outline rect
TextHelper¶
- class pyqode.core.api.DelayJobRunner(delay=500)
Bases: builtins.object
Utility class for running job after a certain delay. If a new request is made during this delay, the previous request is dropped and the timer is restarted for the new request.
We use this to implement a cooldown effect that prevents jobs from being executed while the IDE is not idle.
A job is a simple callable.
- cancel_requests()
Cancels pending requests.
- request_job(job, *args, **kwargs)
Request a job execution. The job will be executed after the delay specified in the DelayJobRunner contructor elapsed if no other job is requested until then.
Parameters: - job (callable) – job.
- args – job’s position arguments
- kwargs – job’s keyworded arguments