API¶
Reader¶
- class fastcsv.Reader(fileobj[, newline=None])¶
Parameters: - fileobj – file-like object. Reader uses only read method.
- newline – same as the one of io.open parameter. See newline parameter.
- Reader.__iter__(self)¶
Just return self.
- Reader.next(self)¶
Return a next row.
- Reader.__enter__(self)¶
- Reader.__exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback)¶
Reader can be treated as a context manager. See Context manager.
newline parameter¶
Reader treats newlines of input object by itself. By default, io.open converts every newlines and carriage returns into “\n”. This is called universal newline mode. So when you read a CSV file which contains a cell like “ab\r\ncd”, this cell value is converted to “ab\ncd”. Sometimes you want to avoid this behaviour.
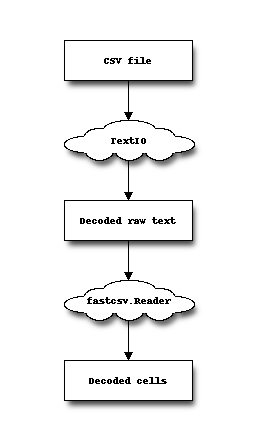
Reader doesn’t convert the newline characters inside the cell. So if you want to leve them as they are, you should specify newline='' in io.open and let the Reader treat newlines.
Examples:
| Input | Reader(open(newline=None)) | Reader(open(newline=’‘)) |
|---|---|---|
| “ab\r\ncd”\r\nef\r\n | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] | [[“ab\r\ncd”], [“ef”]] |
| “ab\ncd”\r\nef\r\n | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] |
| “ab\rcd”\r\nef\r\n | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] | [[“ab\rcd”], [“ef”]] |
| “ab\r\ncd”\ref\r | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] | [[“ab\r\ncd”], [“ef”]] |
| “ab\ncd”\ref\r | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] |
| “ab\rcd”\ref\r | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] | [[“ab\rcd”], [“ef”]] |
| “ab\r\ncd”\nef\n | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] | [[“ab\r\ncd”], [“ef”]] |
| “ab\ncd”\nef\n | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] |
| “ab\rcd”\nef\n | [[“ab\ncd”], [“ef”]] | [[“ab\rcd”], [“ef”]] |
Note
This is the reason why Reader uses read method instead of iteration of fileobj, which is used in csv module. Making newline='' leads you to read the whole file when you iterate over the file.
Context manager¶
Reader can be used as a context manager. It calls close method of fileobj if exists when it exits.
Example:
with fastcsv.Reader(io.open(CSV_FILE)) as reader:
for row in reader:
pass
Writer¶
- class fastcsv.Writer(fileobj[, newline=None[, strict=False]])¶
Parameters: - fileobj – file-like object. Writer uses only write method.
- newline – None, ‘\r\n’, ‘\r’ or ‘\n’. Default is None and it means ‘\r\n’
- strict – Strictly check whether the whole row should be quoted. Not implemented
- Writer.__enter__(self)¶
- Writer.__exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback)¶
Writer can be treated as a context manager. See Writer.writerow().
- Writer.flush(self)¶
- Writer.writerows(self, rows)¶
- Writer.writerow(self, row)¶
Writes a row. Every cells are converted using unicode() except None. None is converted to “”.
Writer have its own cache internally and it should be flushed. You have to call flush to ensure all of the contents be written. If you use Writer as a context manager, it flushes the buffer when it exits.
So, you should write like this:
with io.open(CSV_FILE, 'w', encoding='cp932') as fp: writer = fastcsv.Writer(fp) writer.writerow(row) writer.flush()
or this:
with fastcsv.Writer(io.open(CSV_FILE, 'w', encoding='cp932')) as writer: writer.writerow(row)
It also closes fileobj when it exits.