Automation of Subprocess Debugging and Test-Integration of pydevd.py¶
The PyDev integration module for RemodeDebugServer provides an interface for the automation of the load and application of the pydevd.py module. The PyDev plugin - http://pydev.org - is the utilized embedded component for the debugging of Python based programs within Eclipse - http://eclipse.org .
This includes particularly utilities for cross-process debugging os subprocess calls by PyDev-Remote-Debugging.
Application Basics¶
Remote Debugging with PyDev within Eclipse in the raw form requires the frequent modification of code for clear distinction of development and production systems. The PyDevRDC utilities provide an approach designed to be kept in code from development to production systems.
The feature comprise in more detailed view:
PyDevRDC - PyDev Eclipse Remote Debugging
The main class for integration into the called subprocesses and their simplified setup for debugging based on pydevd.py.
PYDEVD
A predefined object for simple usage.
Interworking and Dependencies¶
The module is foreseen in particular to support the debugging of subprocess calls for the analysis of unit tests.
The call is performed in two basic modes, the fully headless mode ‘cli’ where stdout and stderr are buffered only, and the mode ‘dialogue’, where no buffering is in place. Thus in case of required error analysis a manual call in ‘dialogue’ mode may help.
Design¶
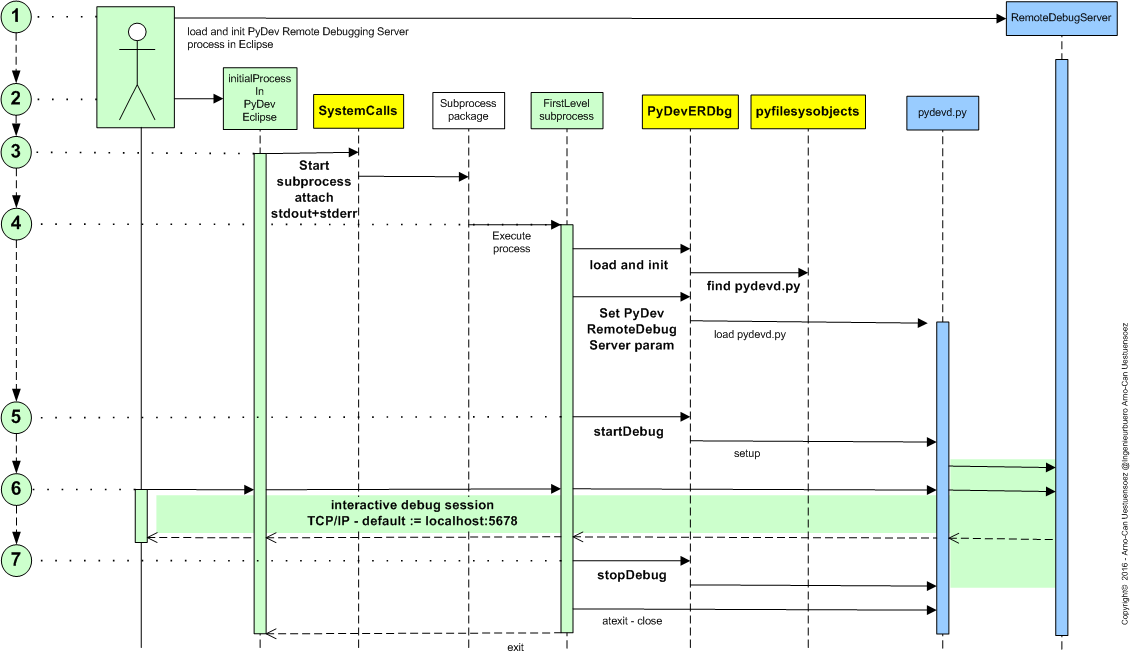
The basic workflow for the integration of processes initially not started under control of ‘pydevd.py’ is depicted in the following figure. Here started by a process from PyDev within Eclipse including the ePyDev package for the automation of the integration and start.
The UseCase ‘UseCases.remote_debug‘ is discussed here in detail, consisting of the components:
- UseCase: CallCase.py [doc] [source]
- Subprocess-Level-0: epyunit4RDbg.py [doc] [source]
- Subprocess-Level-1: myscript.sh [doc] [source]
The following details of the designed control flow contain the required Eclipse/PyDev actions, and the resulting code fragments for the main steps of the control flow for the UseCase ‘UseCases.remote_debug‘. Instead of the subprocess basically any Python based process could be started manually from the commandline and attaches itself to the PyDev plugin of Eclipse.
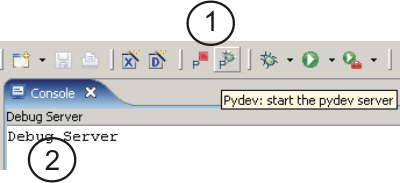
Eclipse-PyDev Framework: Start Remote Debug Server
Start the remote debug server process on the default listenning port localhost:5678.
Copyright by PyDev.org -> Eclipse-PyDev.
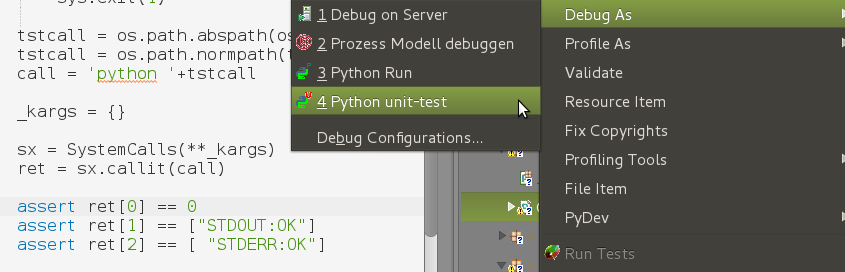
Parent-Process: Start main process
Start the primary process, e.g. for tests by testCase, or a UseCase. The example uses the context menue of PyDev/PyUnit to proceed.
Parent-Process: Start subprocess
Start a process by the subprocess module. This is wrapped into the class ‘epyunit.SystemCalls’, which covers the read of the process output, and the appropriate format transformation for ease of post-analysis of output from unit tests:
# load SystemCalls from epyunit.SystemCalls import SystemCalls # create a controller sx = SystemCalls() # setup subprocess call string call = 'python '+tstcall # execute the subprocess ret = sx.callit(call)
Subprocess: load and init ‘pydevd.py’
Loads and initializes the PyDev stub for the connection to the Eclipse-PyDev gateway ‘pydevd.py’:
# load debug stub-wrapper import epyunit.debug
For the default initial debug controller stub refer to:
epyunit.debug.PYDEVD
The main action is here to detect and/or find and load the module ‘pydevd.py’ provided by PyDev. This depends of whether the process is started under the control of the PyDev debugger, or as a free running process/subprocess. The module is located due to the PyDev manual within the Eclipse plugin subtree at the relative filesystem position:
eclipse/plugins/org.python.pydev_x.x.x/pysrc/pydevd.py
Remark: This may vary e.g. in case of a drop-in installation.
When working with various Eclipse versions the maintenance of the path could become cumbersome. Thus the scan function automates the search and filtering by intermixed ‘re’, and ‘glob’ based path search
epyunit.debug.PYDEVD
For additional information on search options refer to ‘scanEclipseForPydevd’ [doc] [source] .
Subprocess: startDebug
The debug session is started by the execution of the statement:
# start debug session epyunit.debug.PYDEVD.startDebug()
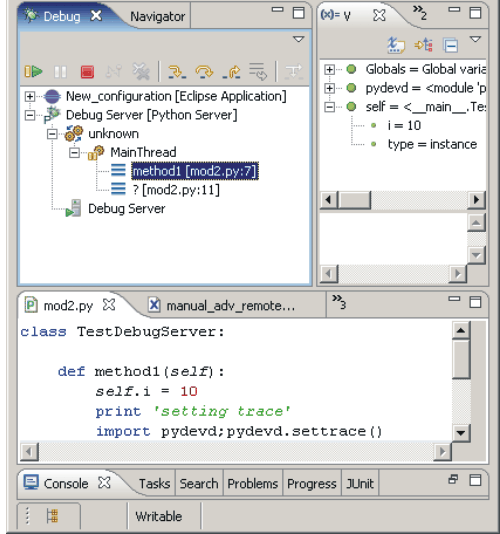
User Dialogue: start interactive session
The debug session is performed by the inspection of an arbitrary number of expressions, e.g. by starting another nested subprocess:
myproc = MySubProcessLevel01(_APPNAME) myproc.execute(_APPNAME)
Debug Session: end debug session
f.f.s. / a.s.a.p.
Another example with Basic Control.
Almost the same as before, but some basic parameters are set for some control.
Include the following statements in the executable to be started by another process:
from epyunit.debug import PYDEVD _pydevdpath=/path/to/your/eclipse/directory _ignore=True _remotedebug=True PYDEVD.startRemoteDebug( pydevdpath=_pydevdpath, ignore=_ignore,remotedebug=_remotedebug, )Start a debugging server, see Remote Debugger @ Eclipse-PyDev.
Copyright by PyDev.org -> Eclipse-PyDev.
Set a breakpoint in the code of the remote process.
Start the caller process, see Remote Debugger @ Eclipse-PyDev.
Copyright by PyDev.org -> Eclipse-PyDev.
Examples¶
EXAMPLES:
- CLI: command line interface
- Eclipse: Executable within Eclipse IDE
- Detailed examples in the subdirectories of the source package:
- tests + testdata
- UseCases