Database API¶
The classes involved in a Dallinger experiment are:
Network, Node,
Vector, Info,
Transmission,
Transformation,
Participant, and
Question. The code for all these classes can
be seen in models.py. Each class has a corresponding table in the
database, with each instance stored as a row in the table. Accordingly,
each class is defined, in part, by the columns that constitute the table
it is stored in. In addition, the classes have relationships to other
objects and a number of functions.
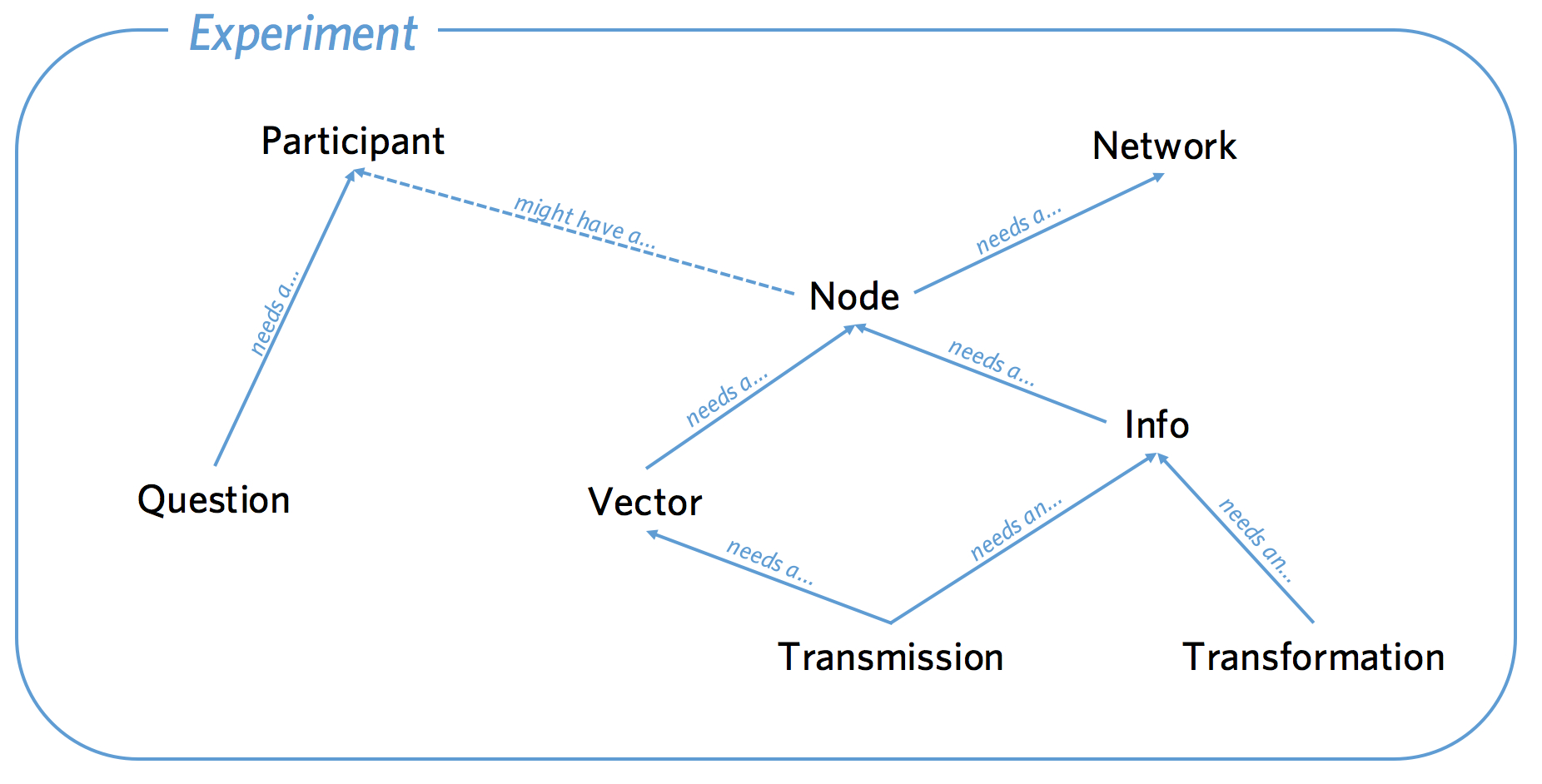
The classes have relationships to each other as shown in the diagram
below. Be careful to note which way the arrows point. A Node is a
point in a Network that might be associated with a Participant.
A Vector is a directional connection between a Node and another
Node. An Info is information created by a Node. A
Transmission is an instance of an Info being sent along a
Vector. A Transformation is a relationship between an Info
and another Info. A Question is a survey response created by a
Participant.
Network¶
The Network object can be imagined as a set of other objects with
some functions that perform operations over those objects. The objects
that Network‘s have direct access to are all the Node‘s in the
network, the Vector‘s between those Nodes, Infos created by those
Nodes, Transmissions sent along the Vectors by those Nodes and
Transformations of those Infos. Participants and Questions do not exist
within Networks. An experiment may involve multiple Networks,
Transmissions can only occur within networks, not between them.
-
class
dallinger.models.Network(**kwargs)[source]¶ Contains and manages a set of Nodes and Vectors etc.
Columns¶
-
Network.type¶ A String giving the name of the class. Defaults to “network”. This allows subclassing.
-
Network.max_size¶ How big the network can get, this number is used by the full() method to decide whether the network is full
-
Network.full¶ Whether the network is currently full
-
Network.role¶ The role of the network. By default dallinger initializes all networks as either “practice” or “experiment”
Relationships¶
-
dallinger.models.Network.all_nodes¶ All the Nodes in the network.
-
dallinger.models.Network.all_vectors¶ All the vectors in the network.
-
dallinger.models.Network.all_infos¶ All the infos in the network.
-
dallinger.models.Network.networks_transmissions¶ All the transmissions int he network.
-
dallinger.models.Network.networks_transformations¶ All the transformations in the network.
Methods¶
-
Network.infos(type=None, failed=False)[source]¶ Get infos in the network.
type specifies the type of info (defaults to Info). failed { False, True, “all” } specifies the failed state of the infos. To get infos from a specific node, see the infos() method in class
Node.
-
Network.latest_transmission_recipient()[source]¶ Get the node that most recently received a transmission.
-
Network.nodes(type=None, failed=False, participant_id=None)[source]¶ Get nodes in the network.
type specifies the type of Node. Failed can be “all”, False (default) or True. If a participant_id is passed only nodes with that participant_id will be returned.
-
Network.size(type=None, failed=False)[source]¶ How many nodes in a network.
type specifies the class of node, failed can be True/False/all.
-
Network.transformations(type=None, failed=False)[source]¶ Get transformations in the network.
type specifies the type of transformation (default = Transformation). failed = { False, True, “all” }
To get transformations from a specific node, see Node.transformations().
Node¶
Each Node represents a single point in a single network. A Node must be within a Network and may also be associated with a Participant.
Columns¶
-
Node.type¶ A String giving the name of the class. Defaults to
node. This allows subclassing.
-
Node.network_id¶ the id of the network that this node is a part of
-
Node.participant_id¶ the id of the participant whose node this is
Relationships¶
-
Node.network¶ the network the node is in
-
Node.participant¶ the participant the node is associated with
-
dallinger.models.Node.all_outgoing_vectors¶ All the vectors going out from this Node.
-
dallinger.models.Node.all_incoming_vectors¶ All the vectors coming in to this Node.
-
dallinger.models.Node.all_infos¶ All Infos created by this Node.
-
dallinger.models.Node.all_outgoing_transmissions¶ All Transmissions sent from this Node.
-
dallinger.models.Node.all_incoming_transmissions¶ All Transmissions sent to this Node.
-
dallinger.models.Node.transformations_here¶ All transformations that took place at this Node.
Methods¶
-
Node._to_whom()[source]¶ To whom to transmit if to_whom is not specified.
Return the default value of
to_whomfortransmit(). Should not return None or a list containing None.
-
Node._what()[source]¶ What to transmit if what is not specified.
Return the default value of
whatfortransmit(). Should not return None or a list containing None.
-
Node.connect(whom, direction='to')[source]¶ Create a vector from self to/from whom.
Return a list of newly created vector between the node and whom.
whomcan be a specific node or a (nested) list of nodes. Nodes can only connect with nodes in the same network. In addition nodes cannot connect with themselves or with Sources.directionspecifies the direction of the connection it can be “to” (node -> whom), “from” (whom -> node) or both (node <-> whom). The default is “to”.Whom may be a (nested) list of nodes.
- Will raise an error if:
- whom is not a node or list of nodes
- whom is/contains a source if direction is to or both
- whom is/contains self
- whom is/contains a node in a different network
If self is already connected to/from whom a Warning is raised and nothing happens.
This method returns a list of the vectors created (even if there is only one).
-
Node.fail()[source]¶ Fail a node, setting its status to “failed”.
Also fails all vectors that connect to or from the node. You cannot fail a node that has already failed, but you can fail a dead node.
Set node.failed to True and
time_of_deathto now. Instruct all not-failed vectors connected to this node, infos made by this node, transmissions to or from this node and transformations made by this node to fail.
-
Node.is_connected(whom, direction='to', failed=None)[source]¶ Check whether this node is connected [to/from] whom.
whom can be a list of nodes or a single node. direction can be “to” (default), “from”, “both” or “either”.
If whom is a single node this method returns a boolean, otherwise it returns a list of booleans
-
Node.infos(type=None, failed=False)[source]¶ Get infos that originate from this node.
Type must be a subclass of
Info, the default isInfo. Failed can be True, False or “all”.
-
Node.mutate(info_in)[source]¶ Replicate an info + mutation.
To mutate an info, that info must have a method called
_mutated_contents.
-
Node.neighbors(type=None, direction='to', failed=None)[source]¶ Get a node’s neighbors - nodes that are directly connected to it.
Type specifies the class of neighbour and must be a subclass of Node (default is Node). Connection is the direction of the connections and can be “to” (default), “from”, “either”, or “both”.
-
Node.receive(what=None)[source]¶ Receive some transmissions.
Received transmissions are marked as received, then their infos are passed to update().
“what” can be:
- None (the default) in which case all pending transmissions are received.
- a specific transmission.
Will raise an error if the node is told to receive a transmission it has not been sent.
-
Node.received_infos(type=None, failed=None)[source]¶ Get infos that have been sent to this node.
Type must be a subclass of info, the default is Info.
-
Node.transformations(type=None, failed=False)[source]¶ Get Transformations done by this Node.
type must be a type of Transformation (defaults to Transformation) Failed can be True, False or “all”
-
Node.transmissions(direction='outgoing', status='all', failed=False)[source]¶ Get transmissions sent to or from this node.
Direction can be “all”, “incoming” or “outgoing” (default). Status can be “all” (default), “pending”, or “received”. failed can be True, False or “all”
-
Node.transmit(what=None, to_whom=None)[source]¶ Transmit one or more infos from one node to another.
- “what” dictates which infos are sent, it can be:
- None (in which case the node’s _what method is called).
- an Info (in which case the node transmits the info)
- a subclass of Info (in which case the node transmits all its infos of that type)
- a list of any combination of the above
- “to_whom” dictates which node(s) the infos are sent to, it can be:
- None (in which case the node’s _to_whom method is called)
- a Node (in which case the node transmits to that node)
- a subclass of Node (in which case the node transmits to all nodes of that type it is connected to)
- a list of any combination of the above
- Will additionally raise an error if:
- _what() or _to_whom() returns None or a list containing None.
- what is/contains an info that does not originate from the transmitting node
- to_whom is/contains a node that the transmitting node does not have a not-failed connection with.
Vector¶
A vector is a directional link between two nodes. Nodes connected by a vector can send Transmissions to each other, but because Vectors have a direction, two Vectors are needed for bi-directional Transmissions.
-
class
dallinger.models.Vector(origin, destination)[source]¶ A directed path that links two Nodes.
Nodes can only send each other information if they are linked by a Vector.
Columns¶
-
Vector.origin_id¶ the id of the Node at which the vector originates
-
Vector.destination_id¶ the id of the Node at which the vector terminates.
-
Vector.network_id¶ the id of the network the vector is in.
Relationships¶
-
Vector.origin¶ the Node at which the vector originates.
-
Vector.destination¶ the Node at which the vector terminates.
-
Vector.network¶ the network the vector is in.
-
dallinger.models.Vector.all_transmissions¶ All Transmissions sent along the Vector.
Methods¶
Info¶
An Info is a piece of information created by a Node. It can be sent along Vectors as part of a Transmission.
Columns¶
-
Info.id¶
-
Info.creation_time¶
-
Info.property1¶
-
Info.property2¶
-
Info.property3¶
-
Info.property4¶
-
Info.property5¶
-
Info.failed¶
-
Info.time_of_death¶
-
Info.type¶ a String giving the name of the class. Defaults to “info”. This allows subclassing.
-
Info.origin_id¶ the id of the Node that created the info
-
Info.network_id¶ the id of the network the info is in
-
Info.contents¶ the contents of the info. Must be stored as a String.
Relationships¶
-
Info.origin¶ the Node that created the info.
-
Info.network¶ the network the info is in
-
dallinger.models.Info.all_transmissions¶ All Transmissions of this Info.
-
dallinger.models.Info.transformation_applied_to¶ All Transformations of which this info is the
info_in
-
dallinger.models.Info.transformation_whence¶ All Transformations of which this info is the
info_out
Methods¶
-
Info._mutated_contents()[source]¶ The mutated contents of an info.
When an info is asked to mutate, this method will be executed in order to determine the contents of the new info created.
The base class function raises an error and so must be overwritten to be used.
-
Info.fail()[source]¶ Fail an info.
Set info.failed to True and
time_of_deathto now. Instruct all transmissions and transformations involving this info to fail.
-
Info.transformations(relationship='all')[source]¶ Get all the transformations of this info.
Return a list of transformations involving this info.
relationshipcan be “parent” (in which case only transformations where the info is theinfo_inare returned), “child” (in which case only transformations where the info is theinfo_outare returned) orall(in which case any transformations where the info is theinfo_outor theinfo_inare returned). The default isall
Transmission¶
A transmission represents an instance of an Info being sent along a Vector. Transmissions are not necessarily received when they are sent (like an email) and must also be received by the Node they are sent to.
-
class
dallinger.models.Transmission(vector, info)[source]¶ An instance of an Info being sent along a Vector.
Columns¶
-
Transmission.origin_id¶ the id of the Node that sent the transmission
-
Transmission.destination_id¶ the id of the Node that the transmission was sent to
-
Transmission.vector_id¶ the id of the vector the info was sent along
-
Transmission.network_id¶ the id of the network the transmission is in
-
Transmission.info_id¶ the id of the info that was transmitted
-
Transmission.receive_time¶ the time at which the transmission was received
-
Transmission.status¶ the status of the transmission, can be “pending”, which means the transmission has been sent, but not received; or “received”, which means the transmission has been sent and received
Relationships¶
-
Transmission.origin¶ the Node that sent the transmission.
-
Transmission.destination¶ the Node that the transmission was sent to.
-
Transmission.vector¶ the vector the info was sent along.
-
Transmission.network¶ the network the transmission is in.
-
Transmission.info¶ the info that was transmitted.
Transformation¶
A Transformation is a relationship between two Infos. It is similar to how a Vector indicates a relationship between two Nodes, but whereas a Vector allows Nodes to Transmit to each other, Transformations don’t allow Infos to do anything new. Instead they are a form of book-keeping allowing you to keep track of relationships between various Infos.
-
class
dallinger.models.Transformation(info_in, info_out)[source]¶ An instance of one info being transformed into another.
Columns¶
-
Transformation.type¶ a String giving the name of the class. Defaults to “transformation”. This allows subclassing.
-
Transformation.node_id¶ the id of the Node that did the transformation.
-
Transformation.network_id¶ the id of the network the transformation is in.
-
Transformation.info_in_id¶ the id of the info that was transformed.
-
Transformation.info_out_id¶ the id of the info produced by the transformation.
Participant¶
The Participant object corresponds to a real world participant. Each person who takes part will have a corresponding entry in the Participant table. Participants can be associated with Nodes and Questions.
-
class
dallinger.models.Participant(worker_id, assignment_id, hit_id, mode)[source]¶ An ex silico participant.
Columns¶
-
Participant.type¶ a String giving the name of the class. Defaults to “participant”. This allows subclassing.
-
Participant.worker_id¶ A String, the worker id of the participant.
-
Participant.assignment_id¶ A String, the assignment id of the participant.
-
Participant.unique_id¶ A String, a concatenation of
worker_idandassignment_id, used by psiTurk.
-
Participant.hit_id¶ A String, the id of the hit the participant is working on
-
Participant.mode¶ A String, the mode in which Dallinger is running – live, sandbox or debug.
-
Participant.end_time¶ The time at which the participant finished.
-
Participant.base_pay¶ The amount the participant was paid for finishing the experiment.
-
Participant.bonus¶ the amount the participant was paid as a bonus.
-
Participant.status¶ String representing the current status of the participant, can be –
working- participant is workingsubmitted- participant has submitted their workapproved- their work has been approved and they have been paidrejected- their work has been rejectedreturned- they returned the hit before finishingabandoned- they ran out of timedid_not_attend- the participant finished, but failed the attention checkbad_data- the participant finished, but their data was malformedmissing_notification- this indicates that Dallinger has inferred that a Mechanical Turk notification corresponding to this participant failed to arrive. This is an uncommon, but potentially serious issue.
Relationships¶
-
dallinger.models.Participant.all_questions¶ All the questions associated with this participant.
-
dallinger.models.Participant.all_nodes¶ All the Nodes associated with this participant.
Methods¶
-
Participant.fail()[source]¶ Fail a participant.
Set
failedtoTrueandtime_of_deathto now. Instruct all not-failed nodes associated with the participant to fail.
-
Participant.infos(type=None, failed=False)[source]¶ Get all infos created by the participants nodes.
Return a list of infos produced by nodes associated with the participant. If specified,
typefilters by class. By default, failed infos are excluded, to include only failed nodes usefailed=True, for all nodes usefailed=all. Note that failed filters the infos, not the nodes - infos from all nodes (whether failed or not) can be returned.
-
Participant.nodes(type=None, failed=False)[source]¶ Get nodes associated with this participant.
Return a list of nodes associated with the participant. If specified,
typefilters by class. By default failed nodes are excluded, to include only failed nodes usefailed=True, for all nodes usefailed=all.
Question¶
A Question is a way to store information associated with a Participant as opposed to a Node (Infos are made by Nodes, not Participants). Questions are generally useful for storing responses debriefing questions etc.
-
class
dallinger.models.Question(participant, question, response, number)[source]¶ Responses of a participant to debriefing questions.
Columns¶
-
Question.type¶ a String giving the name of the class. Defaults to “question”. This allows subclassing.
-
Question.participant_id¶ the participant who made the response
-
Question.number¶ A number identifying the question. e.g., each participant might complete three questions numbered 1, 2, and 3.
-
Question.question¶ the text of the question
-
Question.response¶ the participant’s response. Stored as a string.
