robot Package¶
joints Module¶
Module of all the classes related to physical joints. These are objects that link 2 bodies together.
There are two base abstract classes for all joints: Joint and ActuatedJoint. They are not coupled (at all) with ODE or any other physics or collision library/engine.
The classes that implement at least one of those interfaces are these:
There is also an auxiliary class: JointFeedback.
- class ActuatedJoint(world, inner_joint, body1=None, body2=None)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.joints.Joint
A joint with an actuator that can exert force and/or torque to connected bodies.
This is an abstract class.
Constructor.
Parameters: - world (physics.base.World) –
- inner_joint (ode.Joint) –
- body1 (physics.base.Body) –
- body2 (physics.base.Body) –
- class BallSocket(world, body1, body2, anchor)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.joints.Joint
Constructor.
Parameters: - world (physics.base.World) –
- body1 (physics.base.Body) –
- body2 (physics.base.Body) –
- anchor (3-tuple of floats) – joint anchor point
- class Fixed(world, body1, body2)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.joints.Joint
Constructor.
Parameters: - world (physics.base.World) –
- body1 (physics.base.Body) –
- body2 (physics.base.Body) –
- class Joint(world, inner_joint, body1=None, body2=None)[source]¶
Bases: object
Entity that links 2 bodies together, enforcing one or more movement constraints.
This is an abstract class.
Constructor.
Parameters: - world (physics.base.World) –
- inner_joint (ode.Joint) –
- body1 (physics.base.Body) –
- body2 (physics.base.Body) –
- class JointFeedback(body1, body2, force1=None, force2=None, torque1=None, torque2=None)[source]¶
Bases: object
Data structure to hold the forces and torques resulting from the interaction of 2 bodies through a joint.
All attributes are private. The results (force1, force2, torque1, torque2) are all length-3 tuples of floats.
Constructor.
Parameters: - body1 (physics.base.Body) –
- body2 (physics.base.Body) –
- force1 (3-tuple of floats) –
- force2 (3-tuple of floats) –
- torque1 (3-tuple of floats) –
- torque2 (3-tuple of floats) –
- class Rotary(world, body1, body2, anchor, axis)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.joints.ActuatedJoint
Constructor.
Parameters: - world (physics.base.World) –
- body1 (physics.base.Body) –
- body2 (physics.base.Body) –
- anchor (3-tuple of floats) – joint anchor point
- axis (3-tuple of floats) – rotation axis
- add_torque(torque)[source]¶
Apply torque about the rotation axis.
Parameters: torque (float) – magnitude
- angle[source]¶
Return the angle between the two bodies.
The zero angle is determined by the position of the bodies when joint’s anchor was set.
Returns: value ranging -pi and +pi Return type: float
- angle_rate[source]¶
Return the rate of change of the angle between the two bodies.
Returns: angle rate Return type: float
- set_speed(speed, max_force=None)[source]¶
Set rotation speed to speed.
The joint will set that speed by applying a force up to max_force, so it is not guaranteed that speed will be reached.
Parameters: - speed (float) – speed to set
- max_force (float or None) – if not None, the maximum force the joint can apply when trying to set the rotation speed
- class Slider(world, body1, body2, axis)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.joints.ActuatedJoint
Joint with one DOF that constrains two objects to line up along an axis.
It is different from a Piston joint (which has two DOF) in that the Slider does not allow rotation.
Constructor.
Parameters: - world (physics.base.World) –
- body1 (physics.base.Body) –
- body2 (physics.base.Body) –
- axis (3-tuple of floats) – rotation axis
- class Universal(world, body1, body2, anchor, axis1, axis2)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.joints.Joint
Constructor.
Parameters: - world (physics.base.World) –
- body1 (physics.base.Body) –
- body2 (physics.base.Body) –
- anchor (3-tuple of floats) – joint anchor point
- axis1 (3-tuple of floats) – first universal axis
- axis2 (3-tuple of floats) – second universal axis
sensors Module¶
Module of all the classes related to sensors.
There are base classes for sensors whose source is a body, joint or simulation. It also considers those which read information automatically by subscribing to certain signals.
Some abstract classes are:
Some practical sensors are:
- RotaryJointSensor, JointTorque
- Laser
- GPS, Velometer, Accelerometer, Inclinometer
- KineticEnergy, PotentialEnergy, TotalEnergy, SystemTotalEnergy
It also contains the auxiliary classes SensorData and SensorDataQueue.
- class Accelerometer(body, time_step)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BodySensor
Calculate and retrieve a body’s linear and angular acceleration.
Warning
The provided time_step is used to calculate the acceleration based on the velocity measured at two instants in time. If subsequent calls to on_change are separated by a simulation time period different to the given time_step, the results will be invalid.
- class ActuatedJointSensor(joint)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.JointSensor
Sensor whose source of data is an ActuatedJoint joint.
- class BaseSignalSensor(sender=_Any, autotime=False)[source]¶
Bases: object
Base class for sensors that handle signals with on_send().
Constructor.
Parameters: - sender – object that will send the signal; if it is any_sender, subscription will be to any object
- autotime – if True and _get_time() is not overriden, every measurement’s time will set to the computer time in that instant
- any_sender = _Any¶
- class BaseSourceSensor(source)[source]¶
Bases: object
Abstract base class for all sensors.
Sensor data is stored in a queue (data_queue), and it is usually retrieved after the simulation ends but can be accessed at any time:
measurement = sensor.data_queue.pull()
Warning
Beware that ars.utils.containers.Queue.pull() returns the first element of the queue and removes it.
- on_change(time=None)[source]¶
Build a SensorData object and stores it in the data_queue.
Parameters: time (number or None) – if None, current (computer’s) time is used
- class BodySensor(body)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BaseSourceSensor
Abstract base class for sensors whose source of data is a body.
- class GPS(body)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BodySensor
Retrieve a body’s XYZ position.
- class Inclinometer(body)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BodySensor
Retrieve a body’s pitch and roll.
- class JointForce(sim_joint, sim)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.SingleSignalSensor
Sensor measuring force ‘added’ to a joint.
- signal = 'robot joint post add force'¶
- class JointPower(sim_joint, sim)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.MultipleSignalsSensor
Sensor measuring power applied by a joint (due to force and torque).
- signals = ['robot joint post add torque', 'robot joint post add force']¶
- class JointSensor(joint)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BaseSourceSensor
Abstract base class for sensors whose source of data is a joint.
- class JointTorque(sim_joint, sim)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.SingleSignalSensor
Sensor measuring torque added to a joint.
- signal = 'robot joint post add torque'¶
- class KineticEnergy(body)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BodySensor
Retrieve a body’s kinetic energy, both due to translation and rotation.
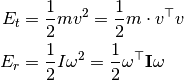
- class Laser(space, max_distance=10.0)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BaseSourceSensor
Laser scanner.
- class MultipleSignalsSensor(signals, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BaseSignalSensor
Abstract base class for sensors subscribed to multiple signals.
Constructor.
Parameters: signals (iterable) – signals to subscribe to
- class PotentialEnergy(body, gravity)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BodySensor
Retrieve a body’s potential energy.
Calculated based on the current position (x) and world’s gravitational acceleration (g).
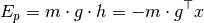
- class RotaryJointSensor(joint)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.ActuatedJointSensor
Sensor measuring the angle (and its rate) of a rotary joint.
- class SensorData(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases: object
Data structure to pack a sensor measurement’s information.
- class SensorDataQueue[source]¶
Bases: ars.utils.containers.Queue
Queue-like container for sensor measurements.
- class SimulationSensor(sim)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BaseSourceSensor
Abstract base class for sensors whose source of data is a simulation.
Constructor.
Parameters: sim (ars.model.simulator.Simulation) – simulation - sim[source]¶
Return the simulation object.
Returns: simulation Return type: ars.model.simulator.Simulation
- class SingleSignalSensor(signal, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BaseSignalSensor
Abstract base class for sensors subscribed to one signal.
Constructor.
Parameters: signal – signal to subscribe to
- class SystemTotalEnergy(sim, disaggregate=False)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.SimulationSensor
Retrieve a system’s total potential and kinetic energy.
It considers all bodies in the simulation. The kinetic energy accounts for translation and rotation.
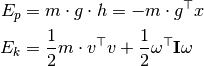
- class TotalEnergy(body, gravity, disaggregate=False)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BodySensor
Retrieve a body’s potential and kinetic energy.
The kinetic energy accounts for translation and rotation.
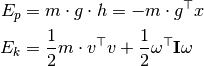
- class Velometer(body)[source]¶
Bases: ars.model.robot.sensors.BodySensor
Calculate and retrieve a body’s linear and angular velocity.
signals Module¶
This module contains string values defining different signals related to the ars.model.robot package.