rpio, the command line tools¶
rpio includes two command-line tools which allow you to inspect and manipulate GPIO’s system wide (including those used by other processes). The BCM GPIO numbering scheme is used by default.
- rpio, a command-line tool to inspect and manipulate GPIOs
- rpio-curses, rpio with a graphical user interface for the terminal
rpio-curses¶
rpio-curses is a graphical user interface for the terminal to inspect and manipulate GPIOs. Its part of RPIO since version 0.8.4. With rpio-curses you can see all GPIOs on the board with function and state, and change every possible parameter. The list is updated every second, and instantly if you change something. You can start rpio-curses in the command line by typing:
$ rpio-curses
Here are a few screenshots of rpio-curses in action:
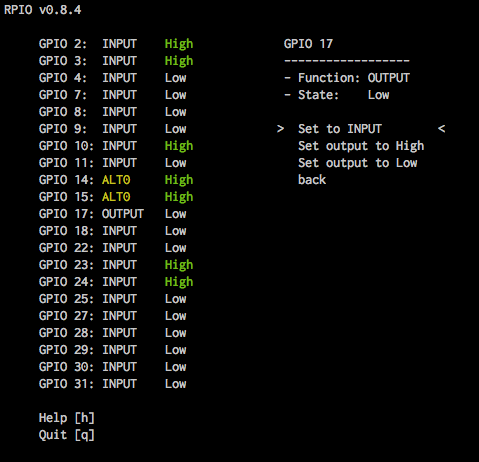
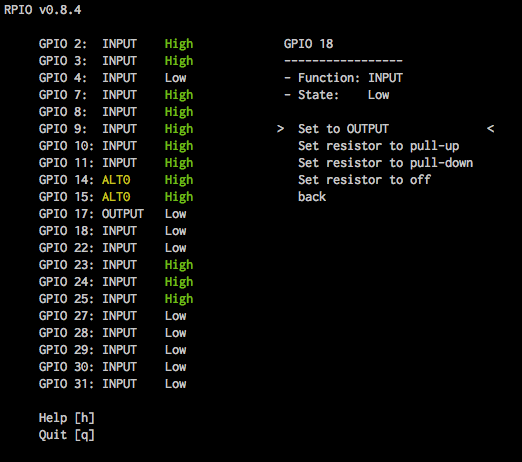
rpio¶
rpio --inspect-all (or -I) is perhaps the most popular command, which shows you all gpios on the board, with function and state. Here is an overview of all the functions of rpio:
Show the help page:
$ rpio -h
Inspect the function and state of gpios (with -i/--inspect):
$ rpio -i 7
$ rpio -i 7,8,9
$ rpio -i 1-9
# Example output for `rpio -i 1-9` (non-existing are ommitted):
GPIO 2: ALT0 (1)
GPIO 3: ALT0 (1)
GPIO 4: INPUT (0)
GPIO 7: OUTPUT (0)
GPIO 8: INPUT (1)
GPIO 9: INPUT (0)
Inspect all GPIO's on this board (with -I/--inspect-all):
$ rpio -I
Set GPIO 7 output to `1` (or `0`) (with -s/--set):
$ rpio -s 7:1
You can only write to pins that have been set up as OUTPUT. You can
set this yourself with `--setoutput <gpio-id>`.
Wait for interrupt events on GPIOs (with -w/--wait_for_interrupts). You
can specify an edge (eg. `:rising`; default='both') as well as `:pullup`,
`:pulldown` or `pulloff`.
$ rpio -w 7
$ rpio -w 7:rising
$ rpio -w 7:falling:pullup
$ rpio -w 7:rising:pullup,17,18
$ rpio -w 1-9
Setup a pin as INPUT (optionally with software resistor):
$ rpio --setinput 7
$ rpio --setinput 7:pullup
$ rpio --setinput 7:pulldown
Setup a pin as OUTPUT (optionally with an initial value (0 or 1)):
$ rpio --setoutput 8
$ rpio --setoutput 8:1
Show Raspberry Pi system info:
$ rpio --sysinfo
# Example output:
000e: Model B, Revision 2.0, RAM: 256 MB, Maker: Sony
You can update the RPIO package to the latest version (equivalent to easy_install -U RPIO):
$ rpio --update-rpio
Install (and update) the rpio manpage:
$ rpio --update-man
$ man rpio